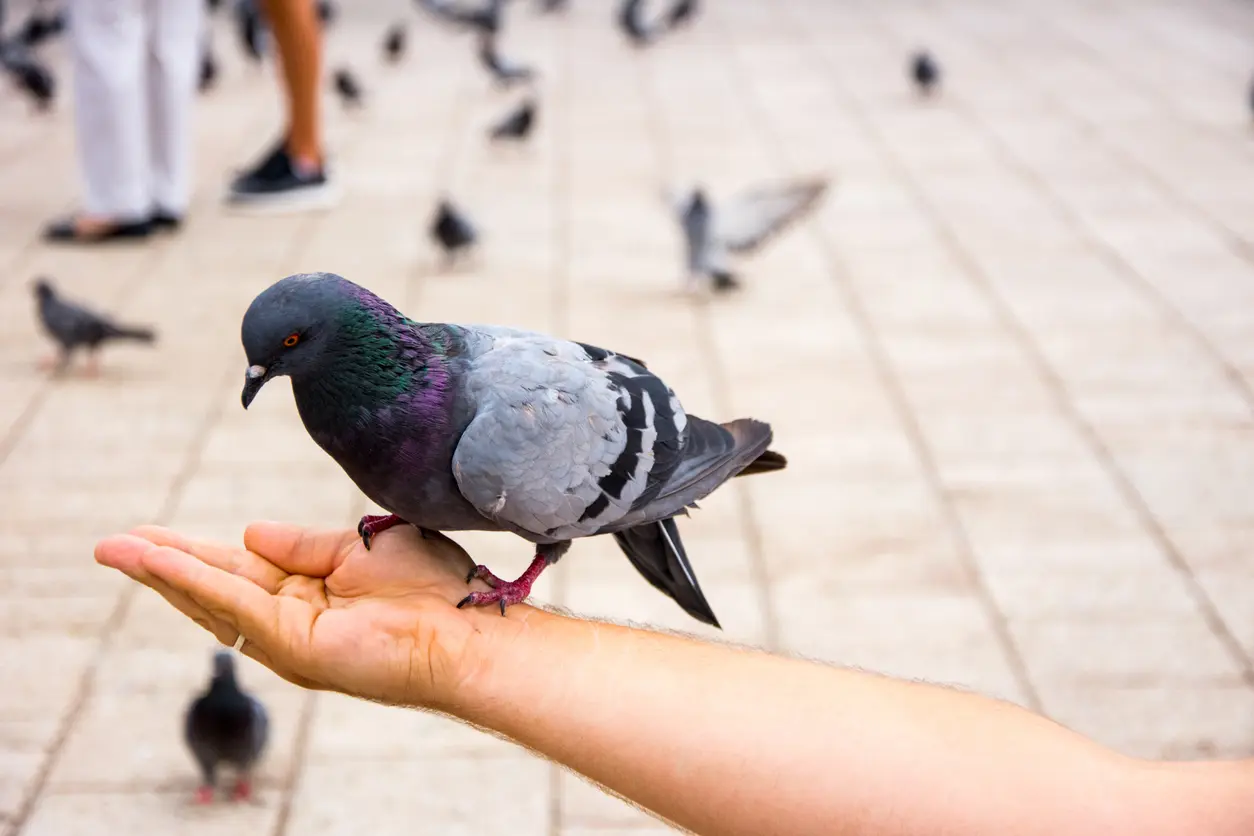
Let me guess. You spotted a bird with a undecorous throne and want to know what type it is. Or, maybe the bird had some undecorous on its head. Either way, youve come to the right place!
This vendible includes wild bird species in the US and Canada with undecorous heads. They could have an unshortened undecorous throne or part of it is blue.
The next step is to identify it.
Ive been yard birding for increasingly than 25 years and have seen many blue-headed birds in my yard so can speak to them. For the remaining bird species, I rely on my trusty sourcebooks and friends at The Cornell Lab of Ornithology to guide me.
Along with each bird listed in this article, a trappy photo of each one is included to help you identify the bird youre interested in.
A range map is moreover included and remoter helps narrow lanugo the species youre laid vision on. If the bird listed doesnt exist in your zone you can probably eliminate it from the running.
It doesnt stop there. This vendible moreover includes a unravelment of each bird, its habitat, diet, nesting habits, and plane what foods itll eat at the feeder (you never know if you want to vamp increasingly of them!).
The range maps are color-coded so you know if its a year-round bird, there to breed, migrating through, or there during a nonbreeding time. Time of year is flipside track to identifying the bird.
My hope is that this vendible will help you hands identify the bird that you saw so lets get at it!
Birds with Undecorous Heads
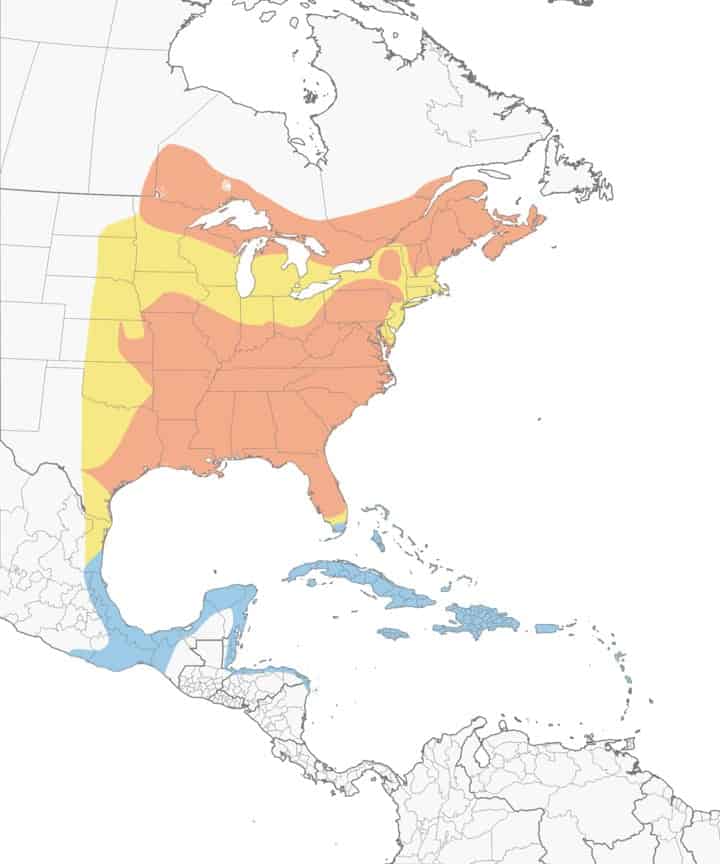
Northern Parula
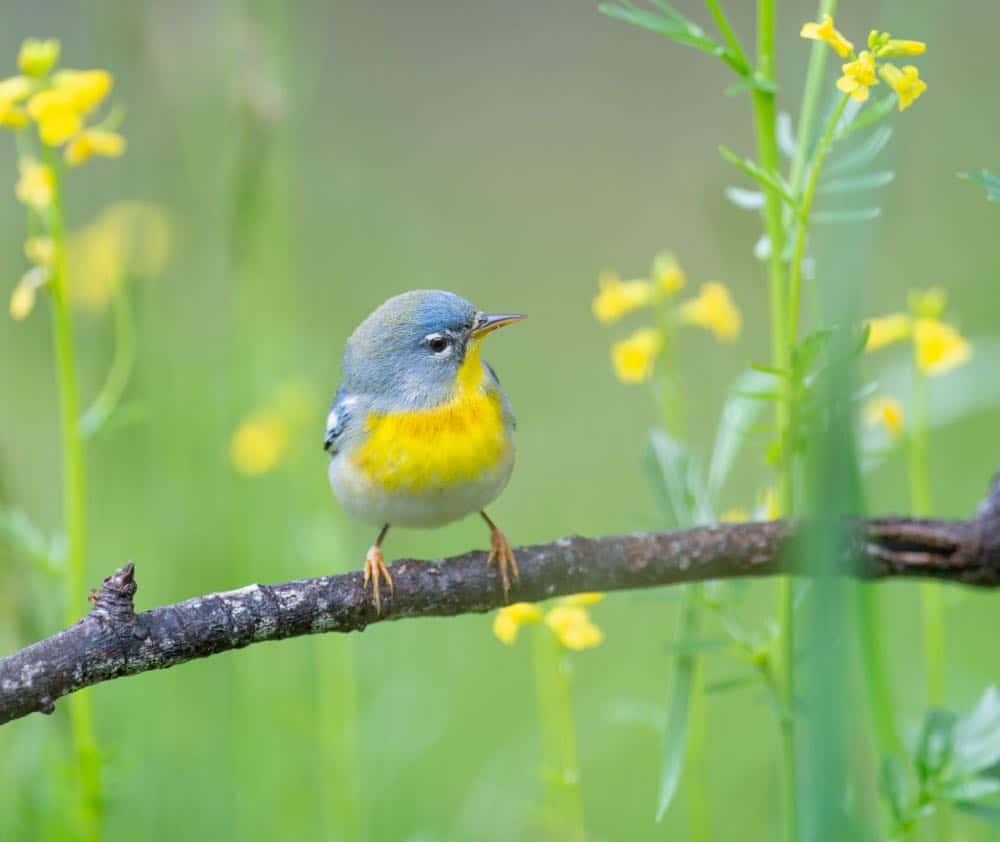

| Appearance | Small bird well-nigh 4.5″ long, blue/gray with a yellow throat and when patch, bluish-gray overall with a yellow-green patch on the back, a brown wreath on lower, white strips whilom and unelevated each eye. Females are similar but increasingly muted colors. neck, and 2 white wing bars. |
| Diet | Spiders, insects, berries, seeds, nectar. |
| Feeder Food | Unlikely to visit a feeder. |
| Habitat | Prefer forested areas expressly when water is present (streams, marshes) and in the lowland where moss is present. |
| Nesting | Nests are built in mossy vegetation as upper up as 100′ at the end of a branch. 1-2 broods/season, 2-7 eggs/brood, eggs are well-nigh .65″ long, white with red/brown/purple speckles and incubation lasts well-nigh 12-14 days. |
Range Map
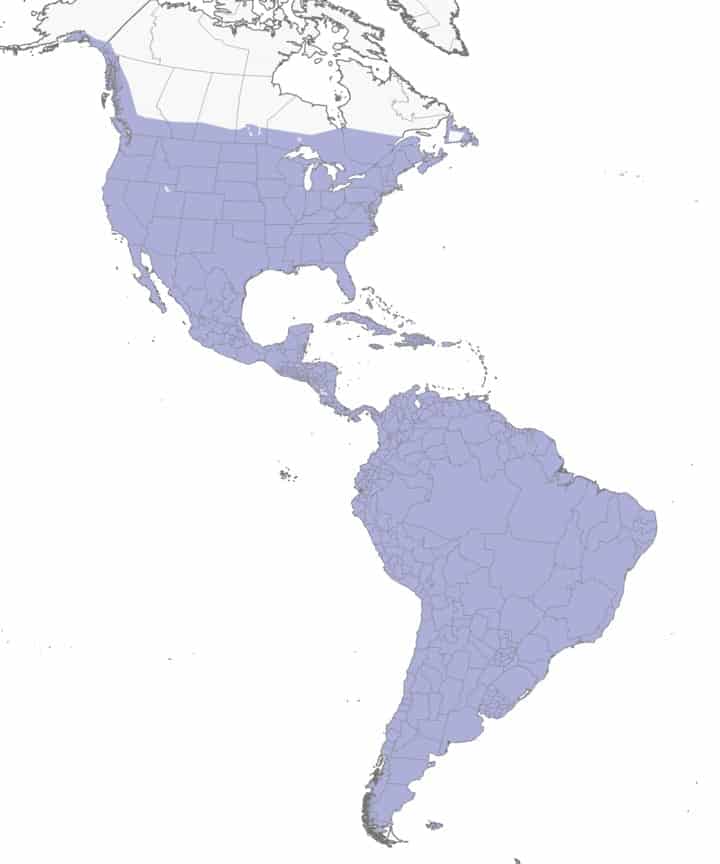
Rock Pigeon
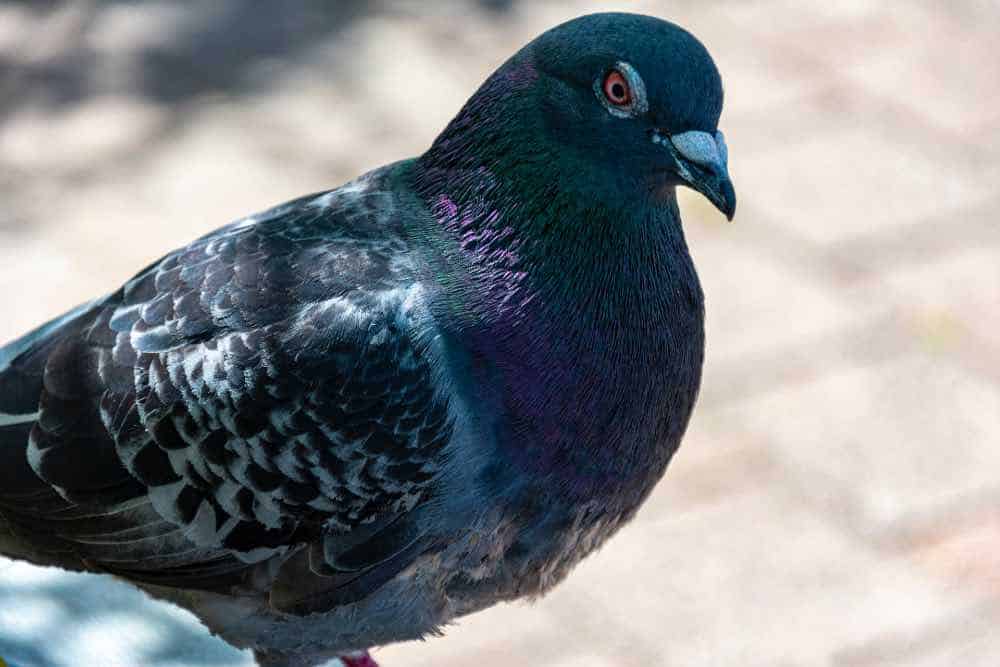

| Appearance | Large bird 12-14″ long, stubby with blue/gray wings with woebegone pointy tips, short red legs, black, round wide tail, and iridescent neck. |
| Diet | Grains, seeds, and fruit. Commonly seen scavenging trash cans for food. |
| Feeder Food | Millet, croaky corn, black-oil sunflower seed, safflower, peanut hearts. |
| Habitat | Common virtually cities and towns as well as farmlands |
| Nesting | A large nest of sticks and grass wherever there’s a ledge (e.g. highway overpass, barns, bridges, tall buildings). 1-6 broods/year, 1-3 eggs/brood, eggs are white, incubation well-nigh 18 days and the young fledge at well-nigh 25-32 days. |
Range Map
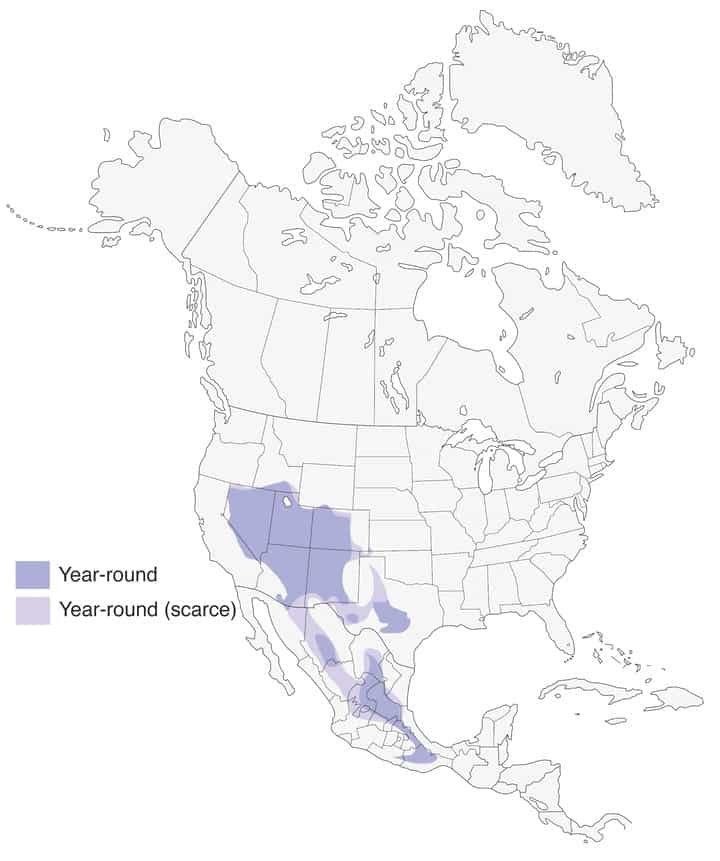
Woodhouse’s Scrub-Jay
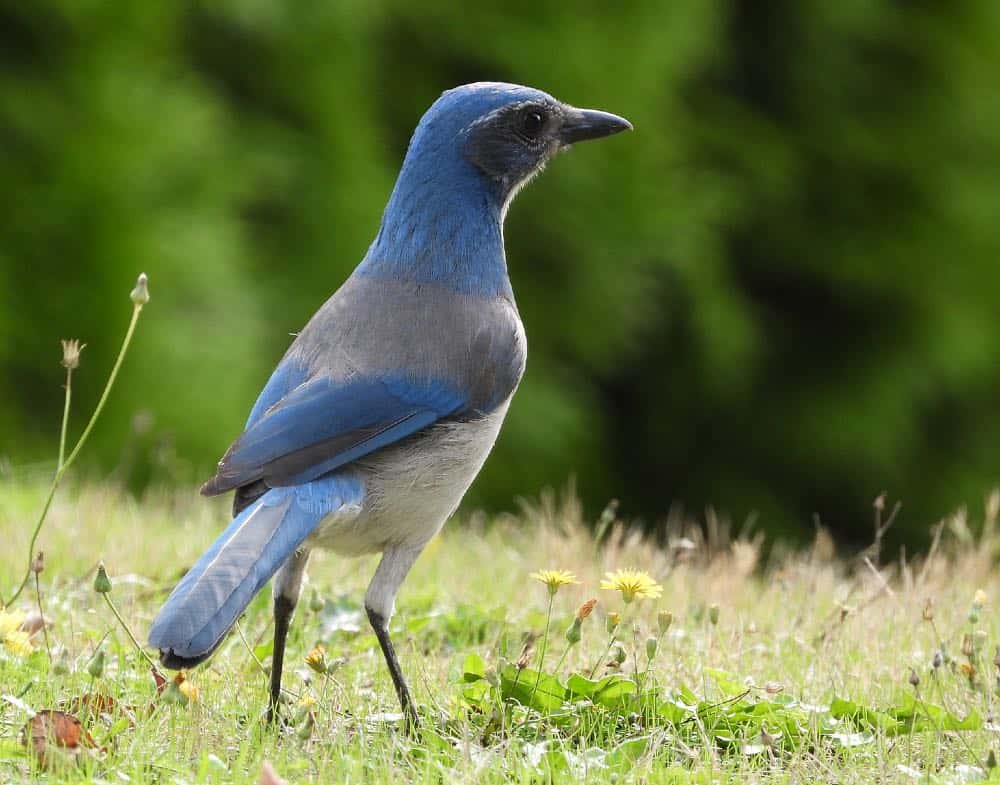

| Appearance | 11-12″ large bird, light undecorous and gray, white throat, gray vitals separated by an indistinct, wilted stripe of unexceptionable undecorous on chest, and long wide tail. Sexuality are similar. |
| Diet | Insects, fruit, nuts, seeds, lizards and nestling birds, sometimes finding nests. |
| Feeder Food | Whole peanuts, sunflower seeds. |
| Habitat | Pinyon pine habitats, dry shrublands of Nevada on south, suburbs and parks. |
| Nesting | Basket shaped nest of twigs and plant in pinyon pine or shrub between 6-14′ up. 1-5 eggs, eggs .9-1.3″ long, stake untried blotched with olive, or stake gray spotted with brown. Incubation 17-19 days and long fledge 17-19 days. |
Range Map
Pinyon Jay
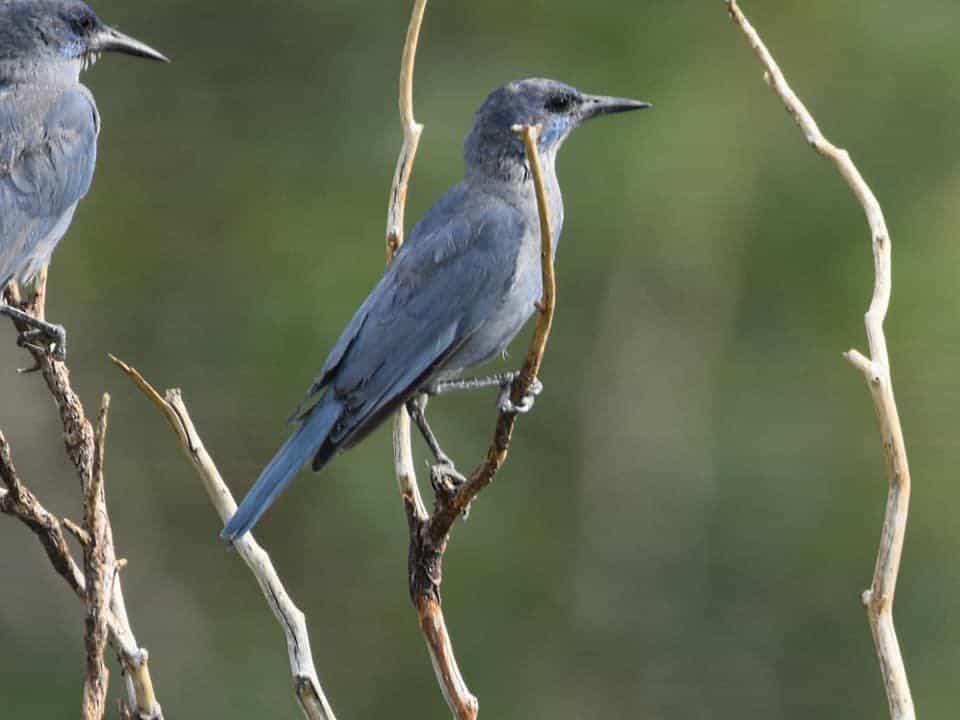

| Appearance | 10-11″ long bird, dusty undecorous soul and lighter undecorous vitals and throat, short tail, and no crown. The sexuality looks similar. |
| Diet | Primarily Pinyon-pine seeds, acorns, fruit, and grains. Moreover consumes insects, lizards, snakes, nestling birds, and small mammals. |
| Feeder Food | Whole peanuts, sunflower seeds, suet, croaky corn. |
| Habitat | Forested areas comprised of Pinyon-juniper, sagebrush, scrub oak, and other pine trees. |
| Nesting | Large unwieldy nests of sticks and twigs in the trees well-nigh 3-115′ up. 1 brood/season, 2-5 eggs/brood, eggs are 1.3-1.5″ long, stake undecorous with visionless brown specks, incubation last 17 days and young fledge between 21-22 days. |
Range Map
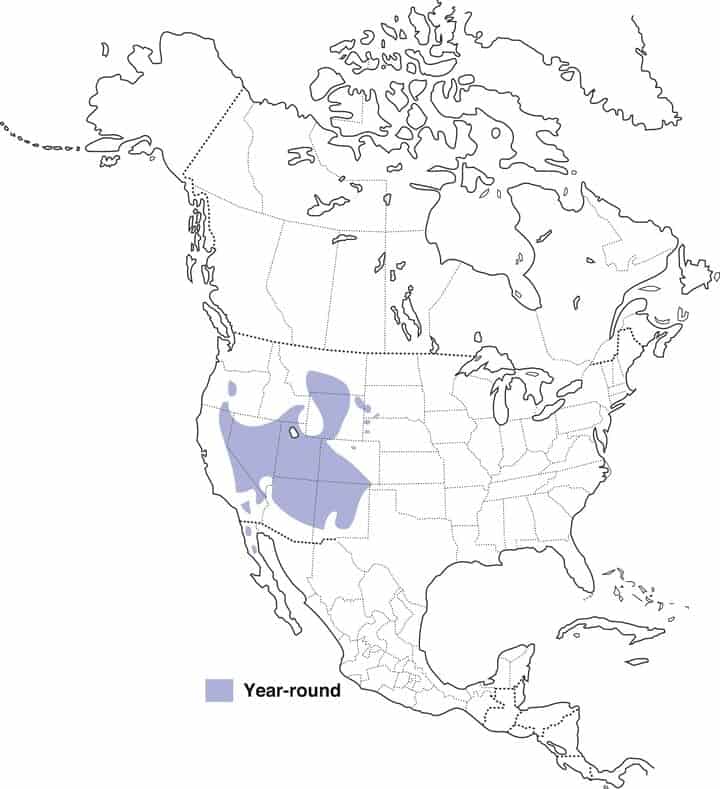
Mexican Jay
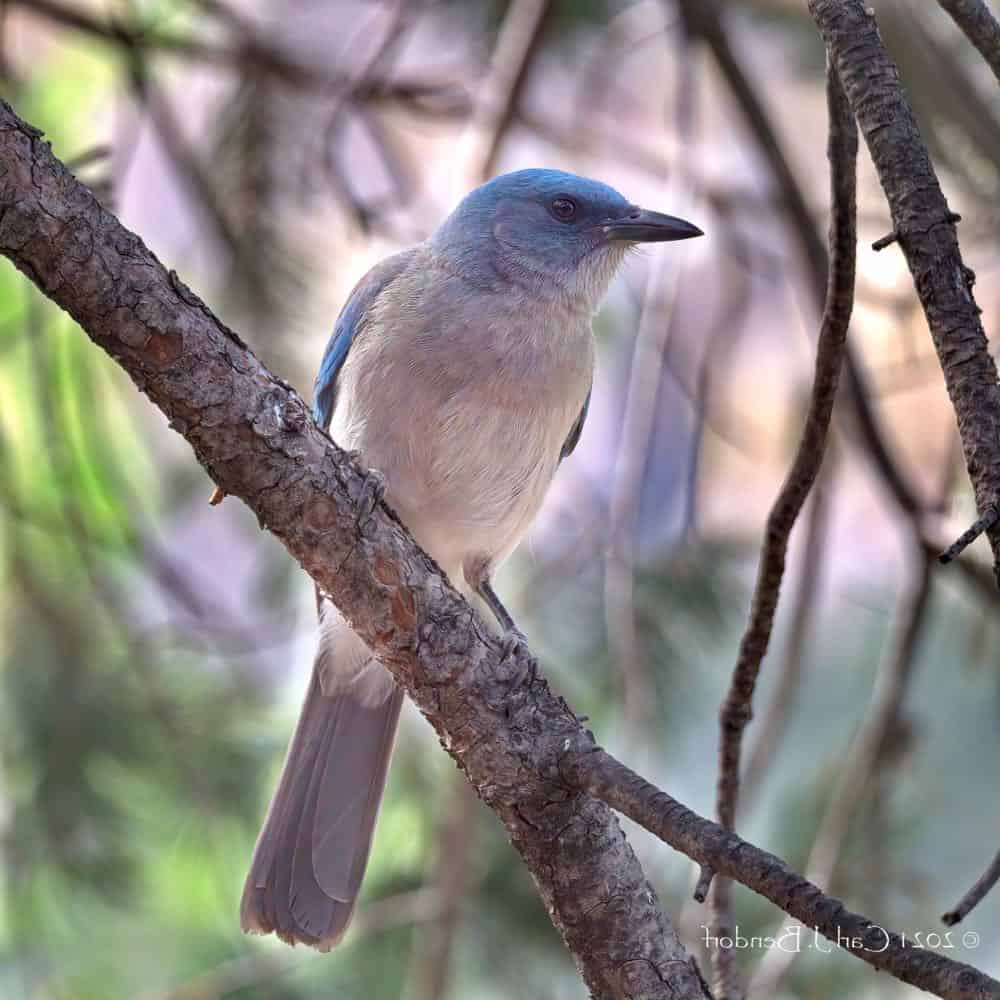

| Appearance | 11.5″ long, large undecorous bird with gray/blue back, soft white underparts and long tail. |
| Diet | Acorns, pinyon nuts, insects, spiders and lizards. |
| Feeder Food | N/A |
| Habitat | Open woodlands near pinyon and oak trees. |
| Nesting | Cup-shaped nest of twigs located tree. 1-6 eggs, eggs are untried with visionless markings but some have no markings. |
Range Map
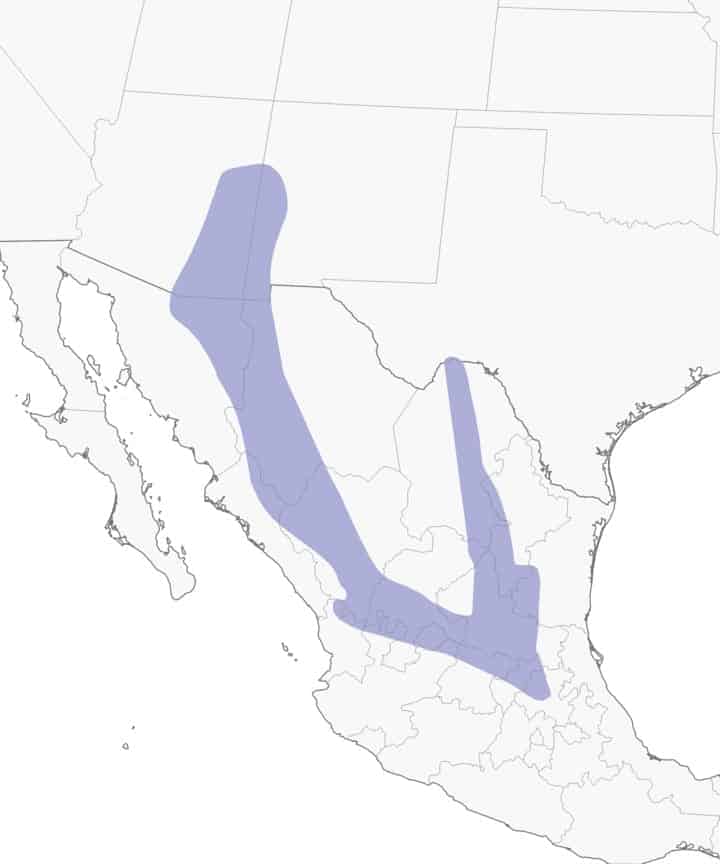
Island Scrub-Jay
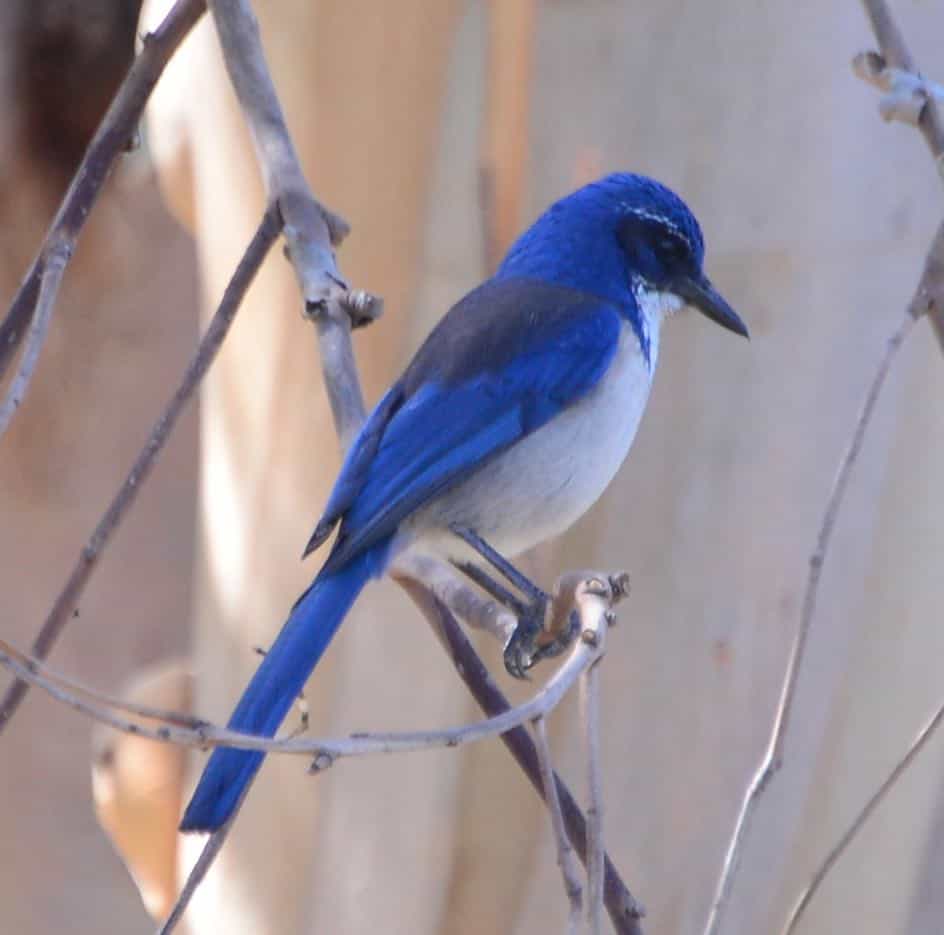

| Appearance | 13″ long, large vibrant undecorous bird, visionless gray when and mask, white throat, light gray belly, large bill, and long tail. Sexuality is similar. |
| Diet | Across, insects, spiders, snakes, lizards, mice, and other birds’ eggs and nestlings. |
| Feeder Food | N/A – Only 2 people inhabit the island. |
| Habitat | Found exclusively on Santa Cruz Island, California. |
| Nesting | Built with sticks, twigs, and roots in dumbo bushes and trees. 2-5 eggs/brood, incubation is well-nigh 20 days. |
Range Map
Found exclusively on Santa Cruz Island, California.
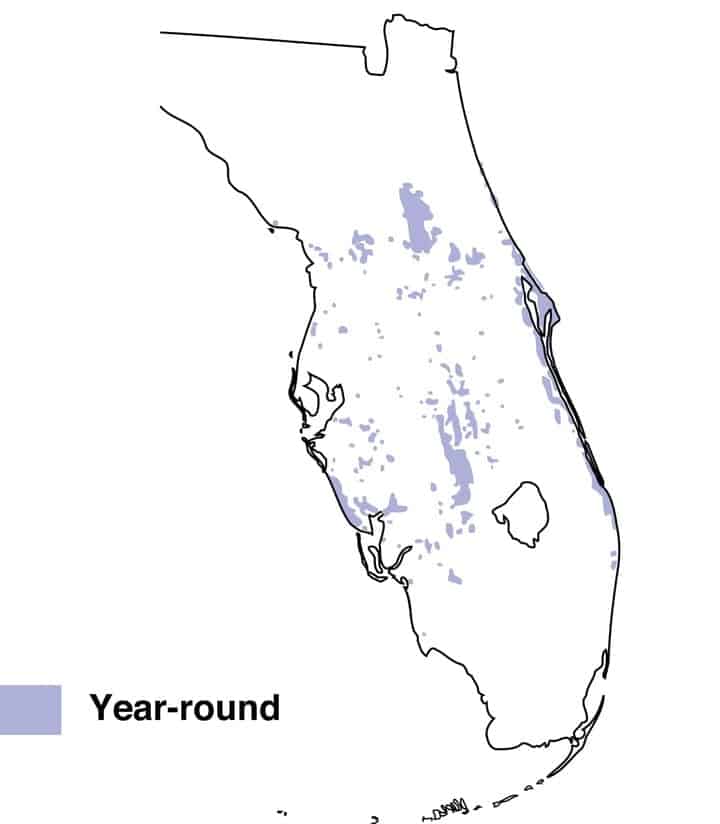
Florida Scrub-Jay
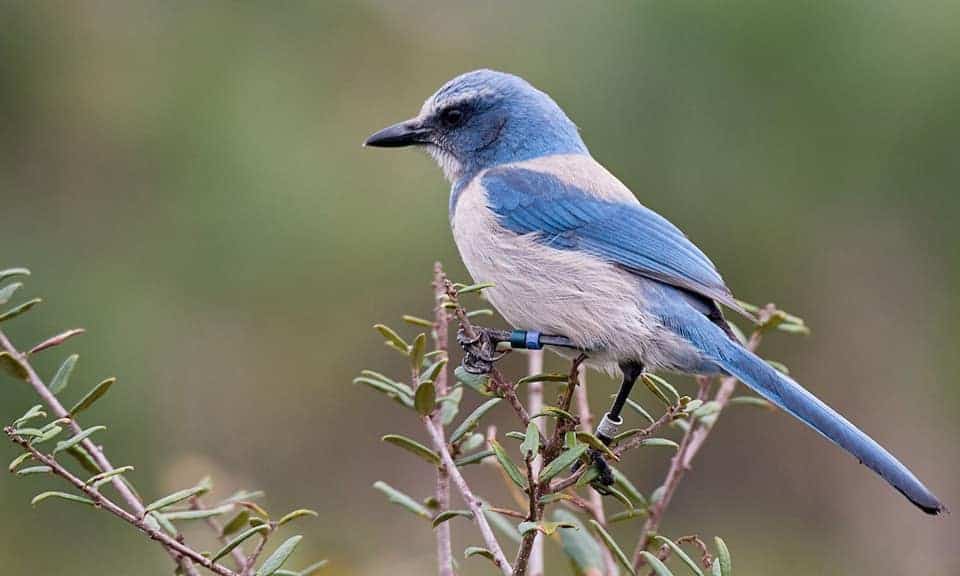

| Appearance | About 10″ long, large undecorous bird, light gray when and belly, swipes of white through forehead, and very long tail. Sexuality is similar. |
| Diet | Varied nutrition of insects, nuts (especially acorns), berries, small snakes, mice, and lizards. |
| Feeder Food | Whole peanuts. |
| Habitat | Low-growing scrub oak exclusively in Florida. |
| Nesting | Cup-shaped nest of twigs and fibers located at the edges of scrubbed areas. 1-2 broods/season, 1-6 eggs/brood, eggs are well-nigh 1″ long, untried with brown spots, 16-21 day incubation and young fledge at well-nigh 12-25 days. |
Range Map
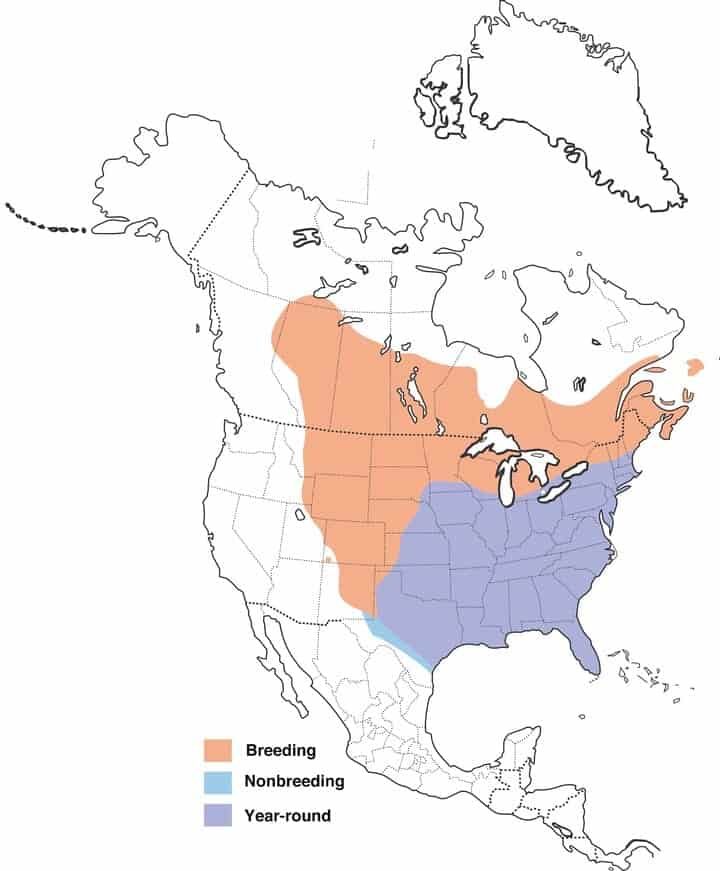
Common Grackle
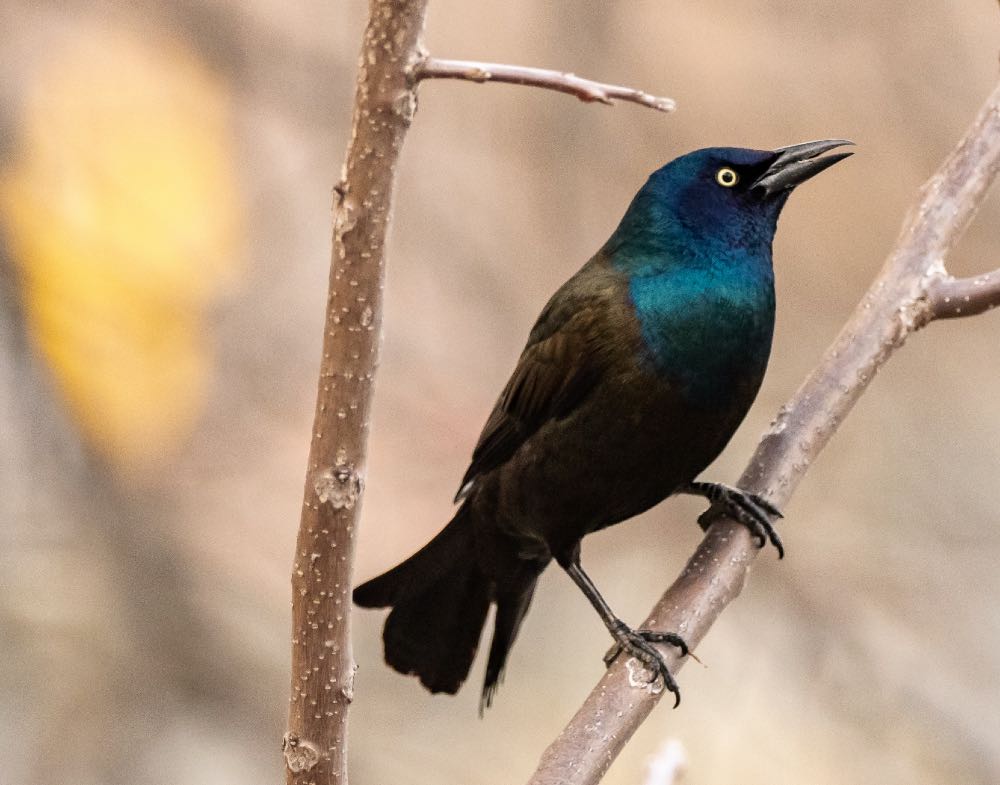

| Appearance | 12.5″ long bird with iridescent undecorous with purple and bronze. Vision are yellow, long flared tail. Sexuality is similar with less vibrant coloring (more brown) and shorter tail. |
| Diet | Insects, grains, seeds, fruit, scavenged garbage. |
| Feeder Food | Sunflower seeds, black-oil sunflower seeds. |
| Habitat | Fields with scattered trees, unshut woodlands, farmlands, and marshes. Worldwide in suburban yards. |
| Nesting | Bulky cup-shaped nest of twigs placed 3-20′ upper in conifer tree. 3-5 eggs incubated for 12-15 days. Young fledge at well-nigh 12-15 days. |
Range Map
California Scrub-Jay
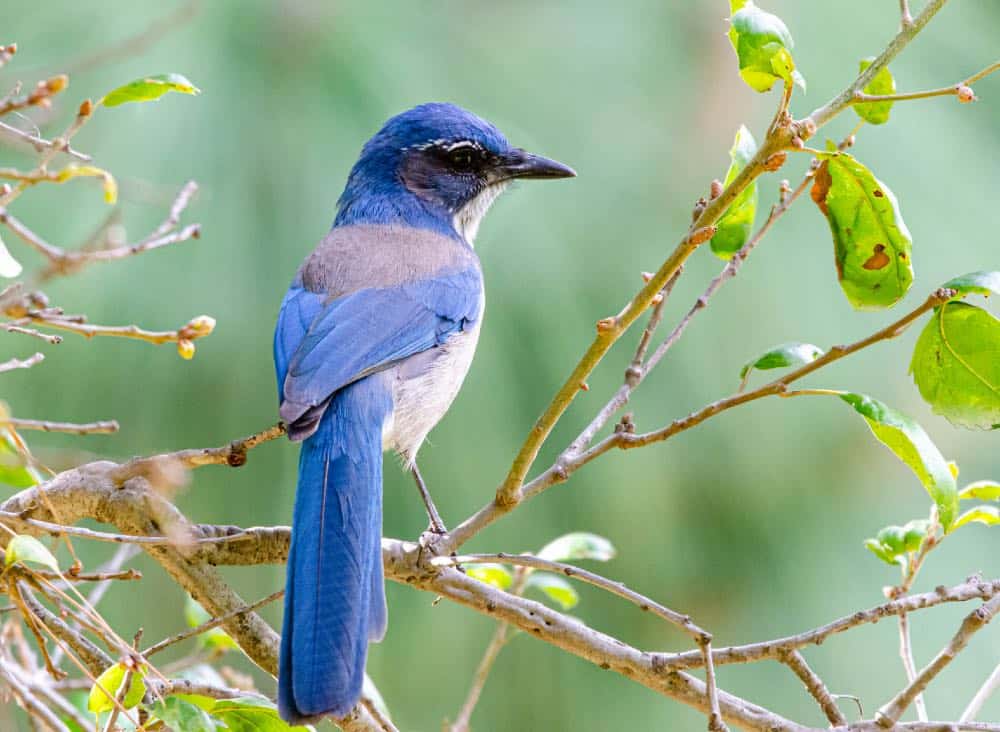

| Appearance | Large bird 11 long, slender, shades of unexceptionable ultramarine undecorous and gray, brown patch on the back, white underparts, undecorous necklace, and long tail. Sexuality squint the same. |
| Diet | Insects, nuts (especially acorns), seeds, fruit, other birds eggs and nestlings and small animals. |
| Feeder Food | Whole peanuts, sunflower seeds, and suet. |
| Habitat | Along the edges of the west tailspin including from Baja, Mexico to the southernmost part of British Columbia. Prefer unshut areas with zaftig trees and scrubs plane within suburban and urban areas. |
| Nesting | Large and unwieldy open-cup nest of twigs and bark, in a tree or small-time well-nigh 3-10′ up. 2-3 eggs/brood, incubated for 15-17 days and young fledge between 18-23 days. Eggs are 1-1.5″ long, stake untried blotched with olive, or stake gray spotted with brown. |
Range Map
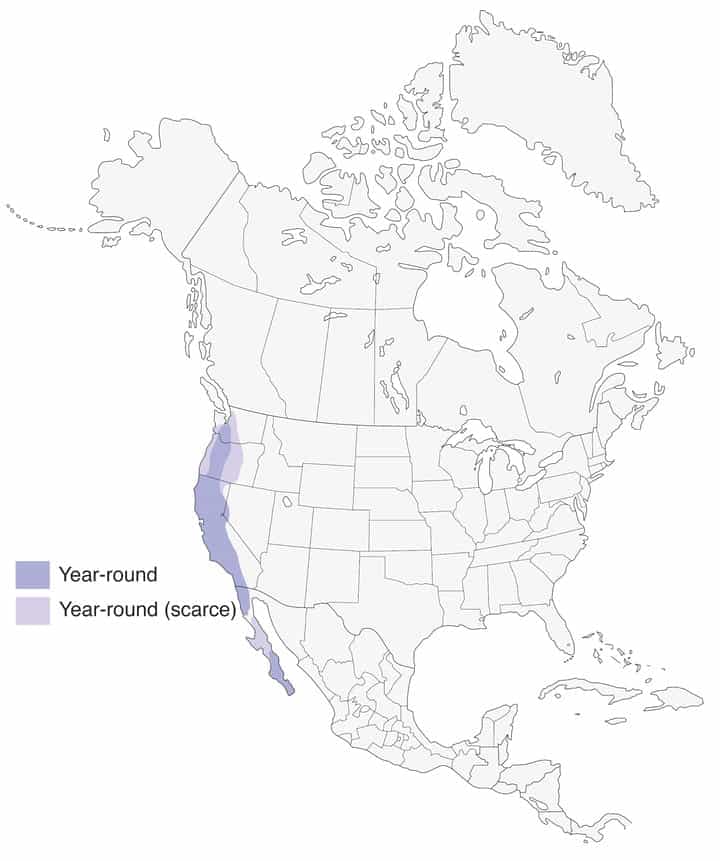
Blue-Gray Gnatcatcher
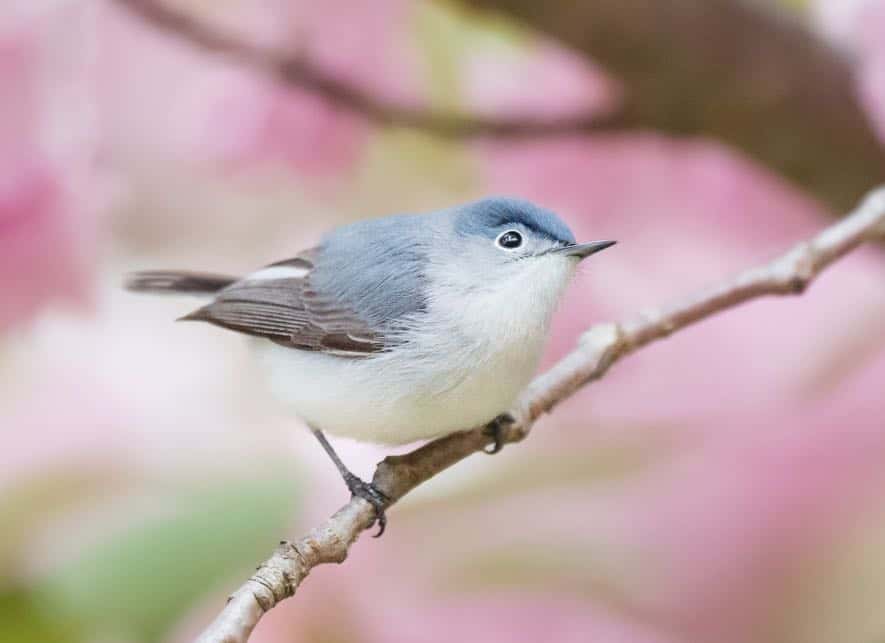

| Appearance | Tiny birds 4.25″ long, soft blue/gray upperparts, white eye-rings, white underparts, long woebegone long tail with white under. Females are the same. The tastefulness male is accented with narrow woebegone eyebrows. |
| Diet | Insects and spiders. |
| Feeder Food | Unlikely to visit the feeder. |
| Habitat | Deciduous forested areas. |
| Nesting | Nest: Tidy cup-shaped nest of natural fibers, bark, and spiderweb well-nigh 3-80′ upper in a tree or shrub. Broods: 1-2 broods/season Clutch: 3-5 eggs/brood Egg color: Stake undecorous with red/rown spots. Egg size: 0.5 – 0.6 inches by 0.4 – 0.5 inches Incubation: 11-15 days and the young fledge at well-nigh 10-15 days. |
Range Map
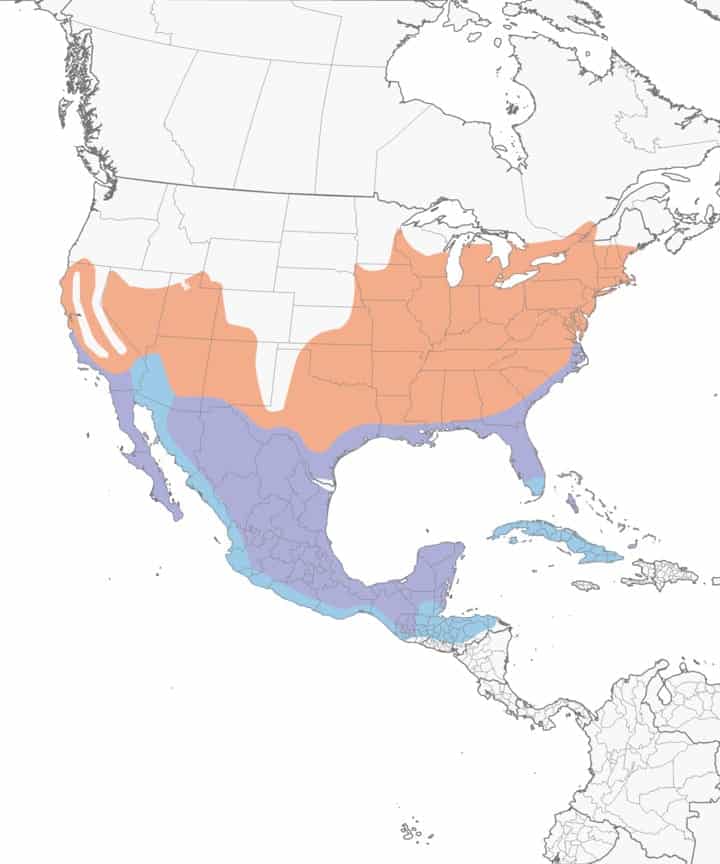
Belted Kingfisher
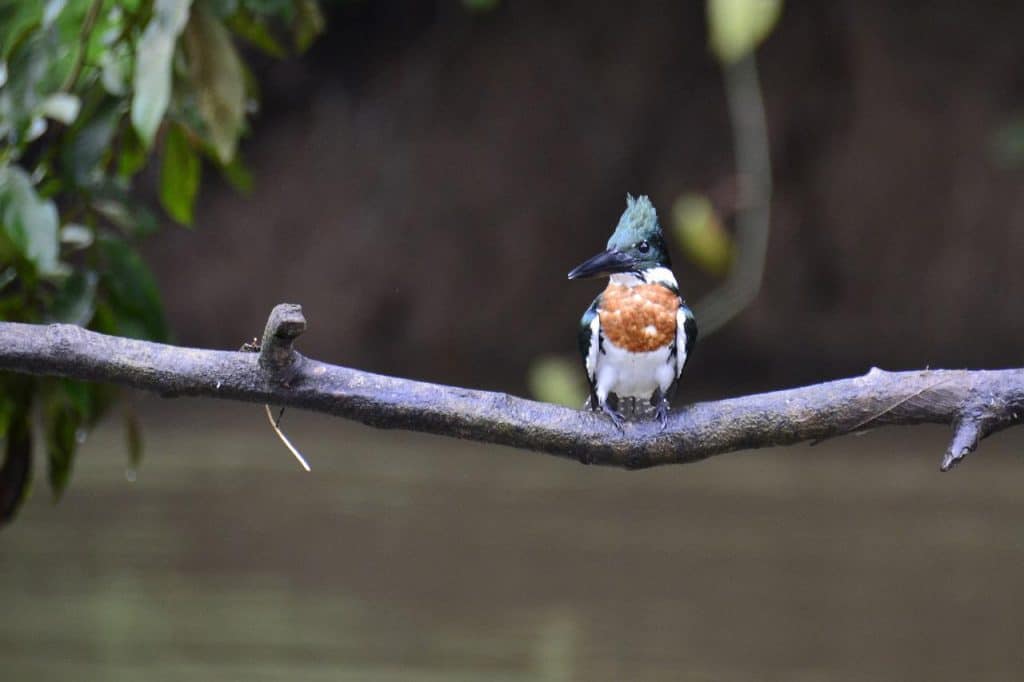

| Appearance | Large 13″ long bird with a large head, long bill, and stocky body. Blue/gray throughout with white ring virtually neck and white chest. Sexuality is same but with spare titian wreath on chest. |
| Diet | Mostly fish with some crustaceans, insects, amphibians, reptiles, young birds, small mammals, and berries. |
| Feeder Food | Unlikely to come to the feeder but often attracted to yards with streams or ponds. |
| Habitat | Near streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, and wifely marine waters – expressly unclouded water with little vegetation. |
| Nesting | Dig burrows withal waters edge. 1-2 broods/season, 5-8 eggs/brood – large white slick eggs (1.5″ long), 22-24 days incubation. |
Range Map
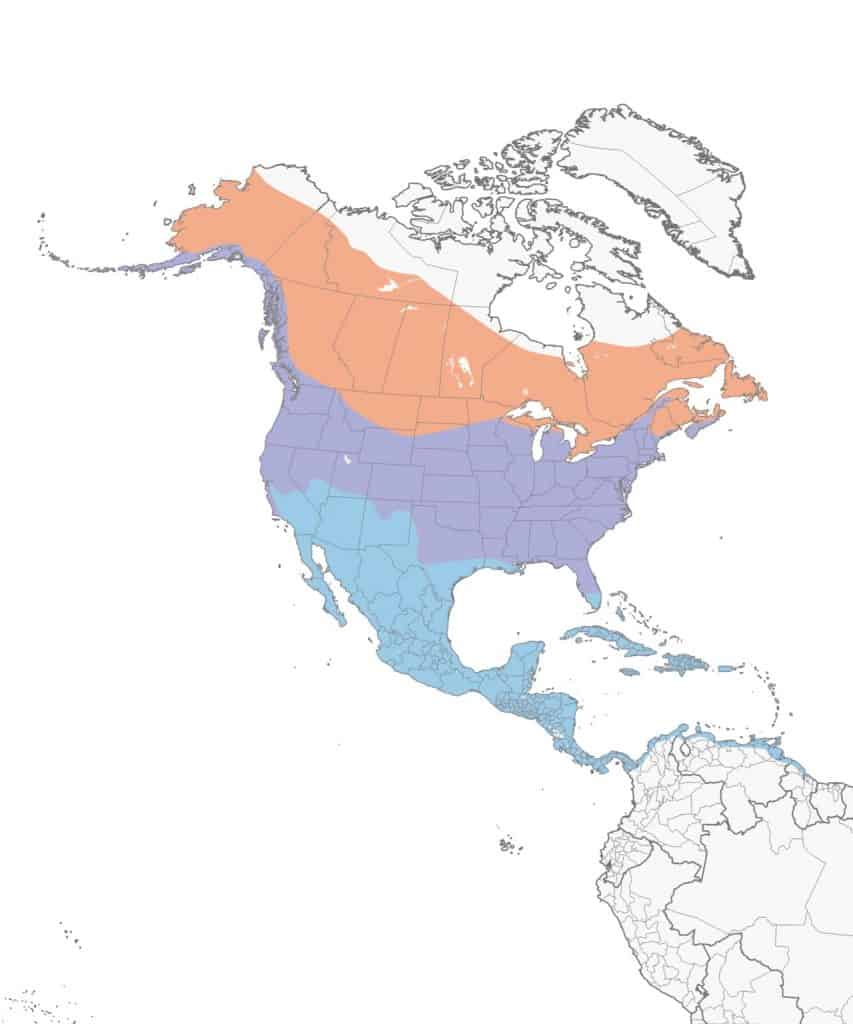
Barn Swallow
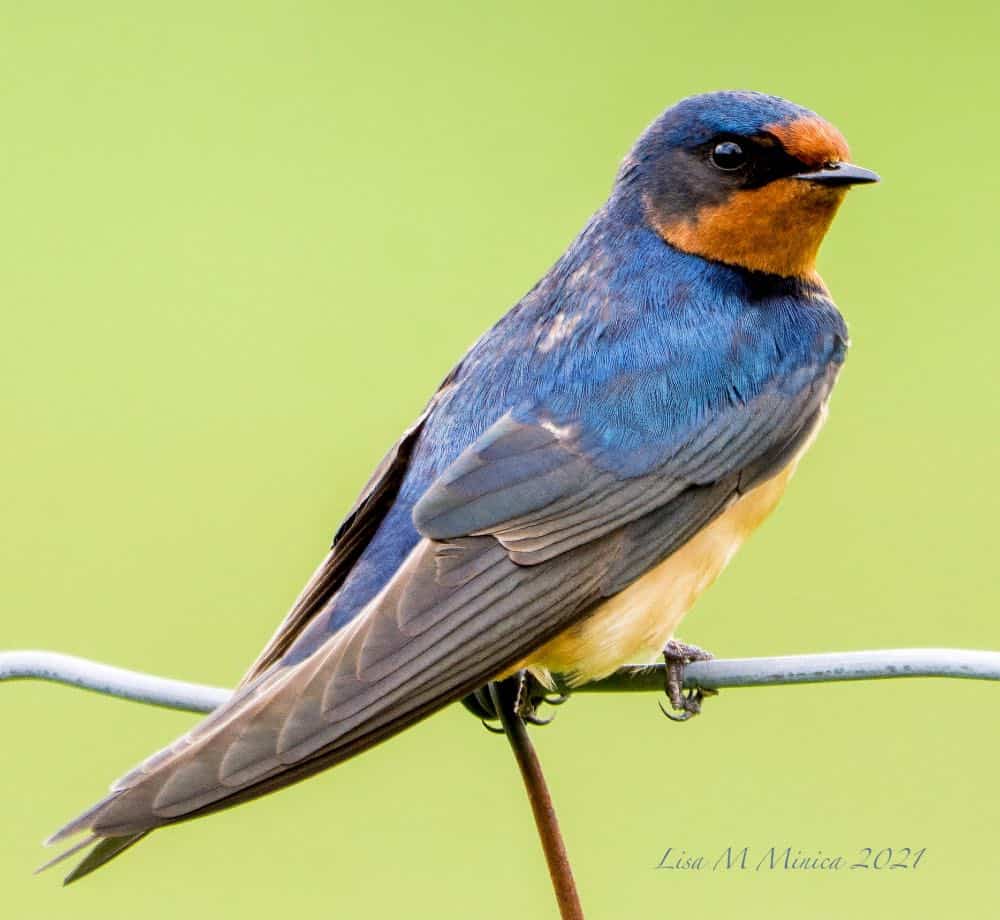

| Appearance | 7″ long, steel undecorous slick on top, titian forehead and throat, and rust-orange underparts. Long forked tail with a white base. The female’s coloring is lighter and the tail shorter. |
| Diet | Insects, preferably beetles, wasps, and flies. Drinks by skimming the surface of the water. |
| Feeder Food | Not likely to visit a feeder. |
| Habitat | Open fields and pastures. |
| Nesting | Typically nests in or on a manmade structure such as a barn. Builds nests of mud. 2 broods/season, 4-5 eggs per brood, eggs are white with brown markings, incubation from 13-17 days. |
Range Map
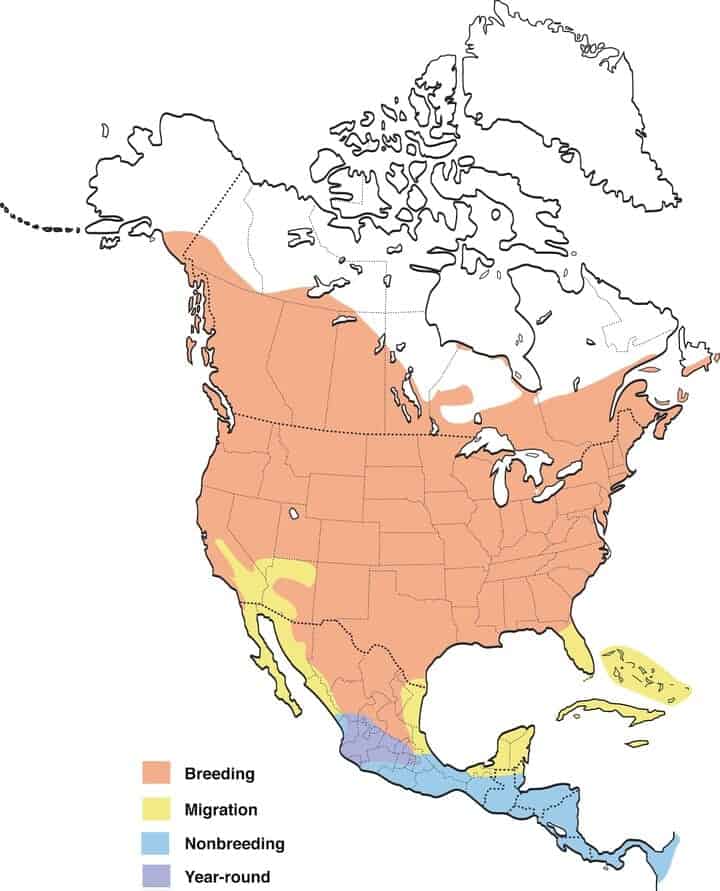
Lazuli Bunting
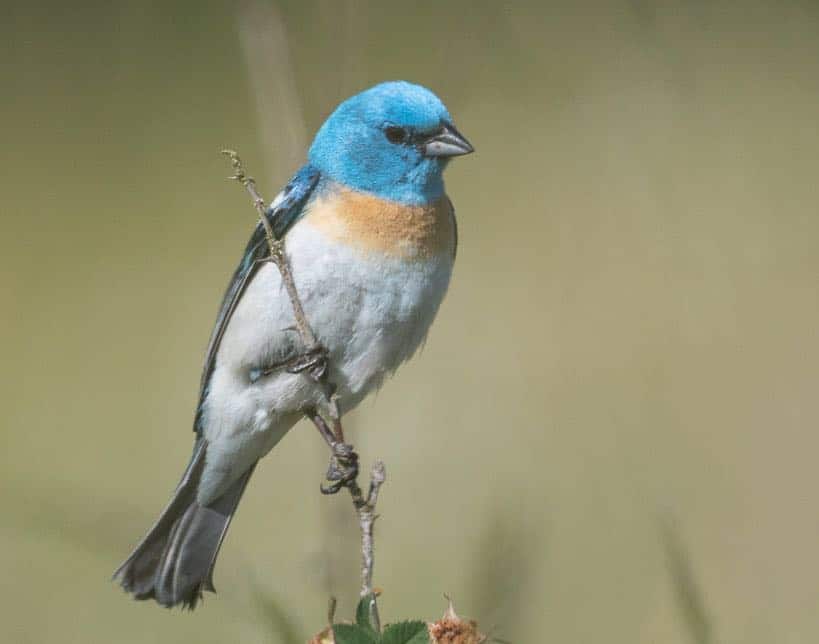

| Appearance | Small bird 5-6″ long, sunny undecorous on top, soft orange-cinnamon verisimilitude chest, white vitals and patch on the shoulder, tapering bill, and slightly unappetizing forehead. |
| Diet | Insects, fruits, and grasses. |
| Feeder Food | White proso millet, sunflower seeds, or nyjer thistle seeds. |
| Habitat | Open woodlands, brushy hillsides, thickets, and backyards throughout the West. |
| Nesting | Cup-shaped nest of bark, twigs, and leaves nestled in a shrub well-nigh 3′ up. They have 1-2 broods/season, 3-4 eggs/brood, and eggs are .7-.8″ long and stake undecorous to faint green/blue or white. 11-14 days incubation period. |
Range Map
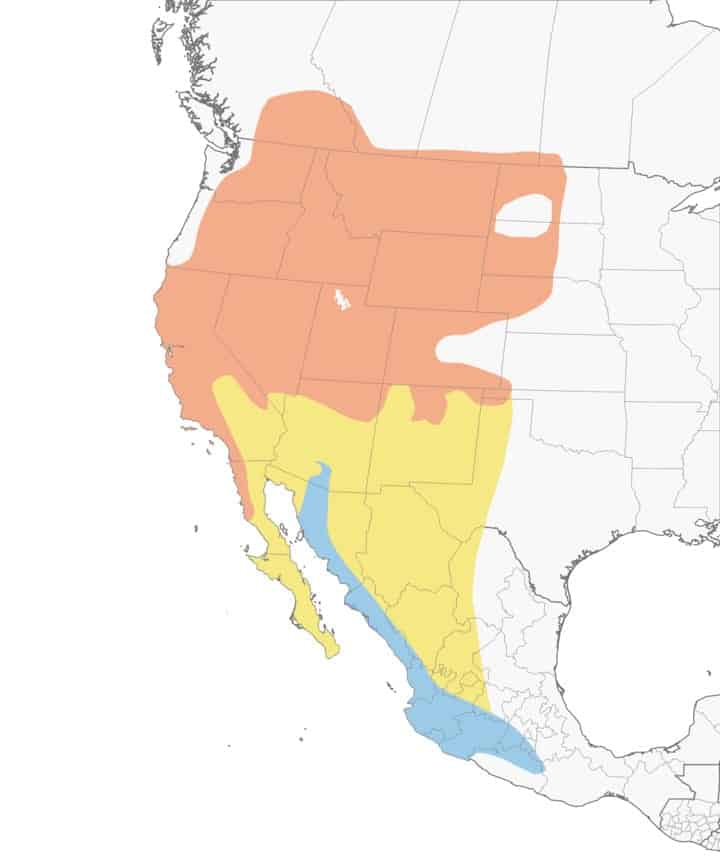
Black Throated Undecorous Warbler
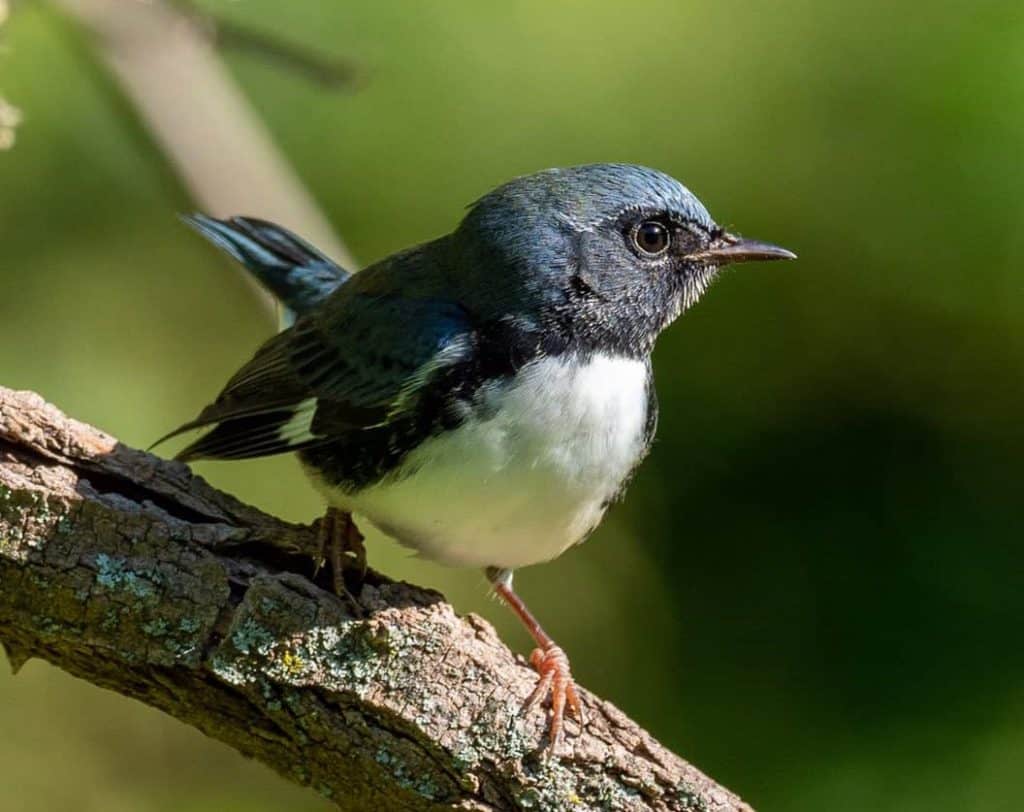

| Appearance | 5″ long, midnight/steel undecorous back, woebegone throat, white belly |
| Diet | Insects and fruit. |
| Feeder Food | Suet, peanut butter, and nectar. |
| Habitat | Prefer mature deciduous and mixed evergreen woodlands with plenty of thick shrubs. |
| Nesting | Cup-shaped nest in shrub made of yelp and spider webs. 1-3 broods/season, 2-5 eggs/brood, eggs are small .6″-.8″, linty white and speckled. 12-13 days incubation and fledges at x |
Range Map
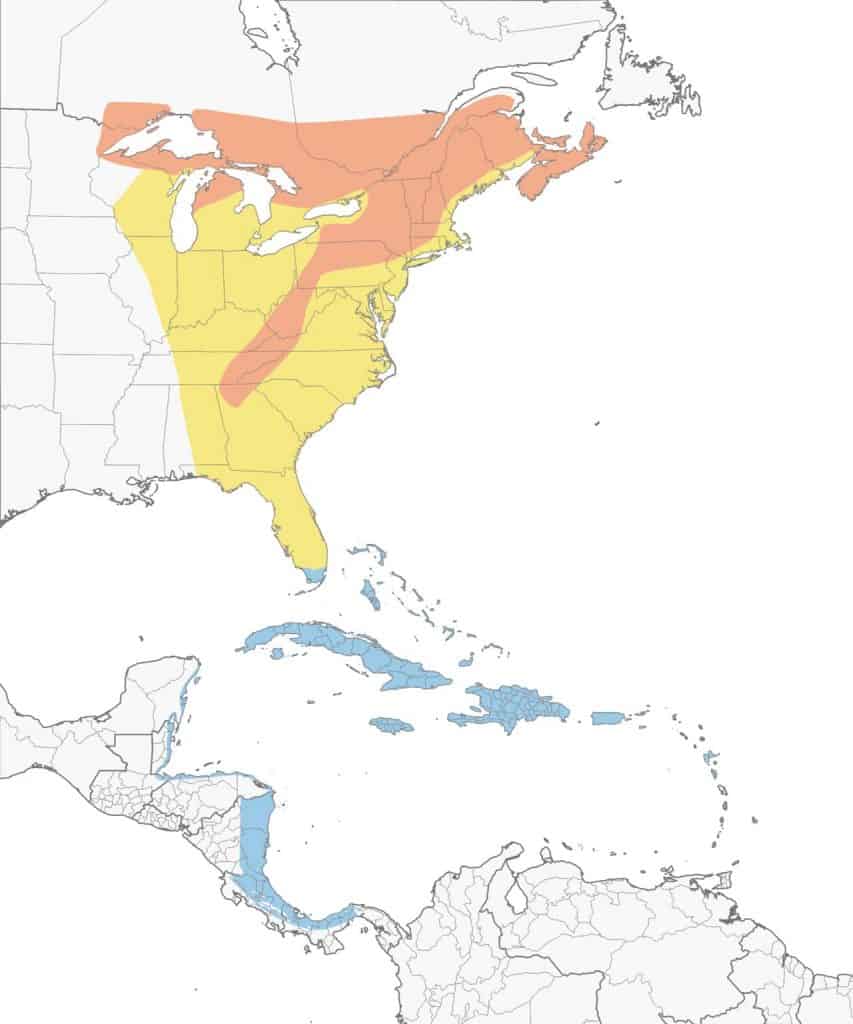
Cerulean Warbler

| Appearance | Small 4.3″ long bird, sky-blue above, white wing bars, darker undecorous streaks on back, white belly, steel/blue neck wreath & stripes on the sides. Females are light blue/green above, soft yellow belly, brown wings, and a bit of white under the eye. |
| Diet | Insects and plants. |
| Feeder Food | Unlikely to visit feeder. |
| Habitat | Deciduous forests with mature tall trees. |
| Nesting | Cup-shaped nests of twigs, grass and spiderwebs placed in tree 16-115′ up. 1 brood/season, 1-5 eggs/brood, eggs are .6-.8″ long, gray/green and speckled with brown, incubation lasts 11-12 days. |
Range Map
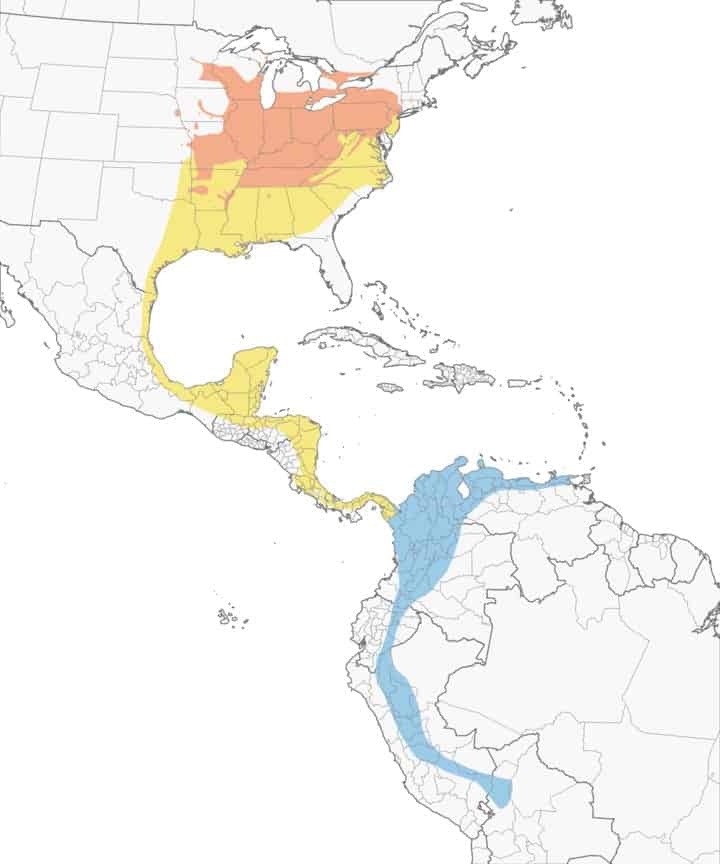
Tree Swallow
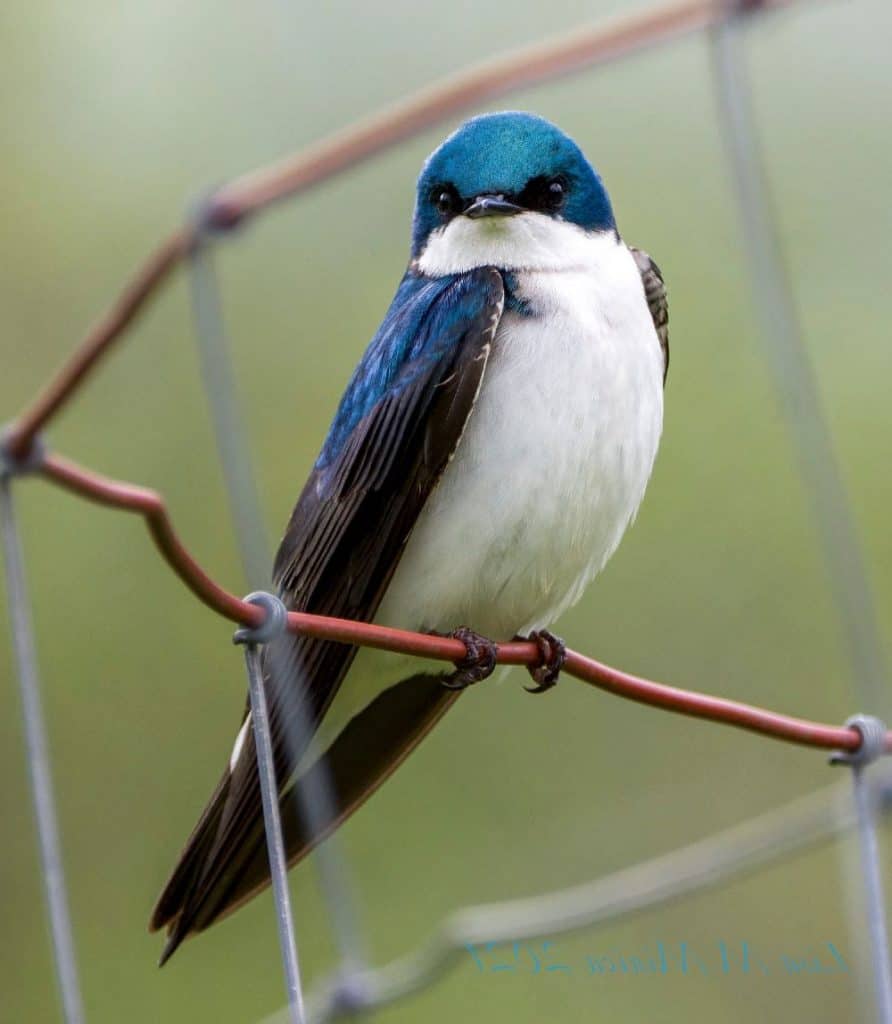

| Appearance | 5-6″ long, visionless metallic undecorous – blue/green with white belly, notched tail and pointed wing tips. Females have same coloring but a bit duller. |
| Diet | Insects and small fruits. |
| Feeder Food | Unlikely to visit a feeder. |
| Habitat | Open areas such as fields, large lawns, and marshes. |
| Nesting | Cavity nester, will use a manmade nest box or natural woodpecker tree hold. 1 brood/season, 4-6 white eggs, 13-16 days of incubation. |
Range Map
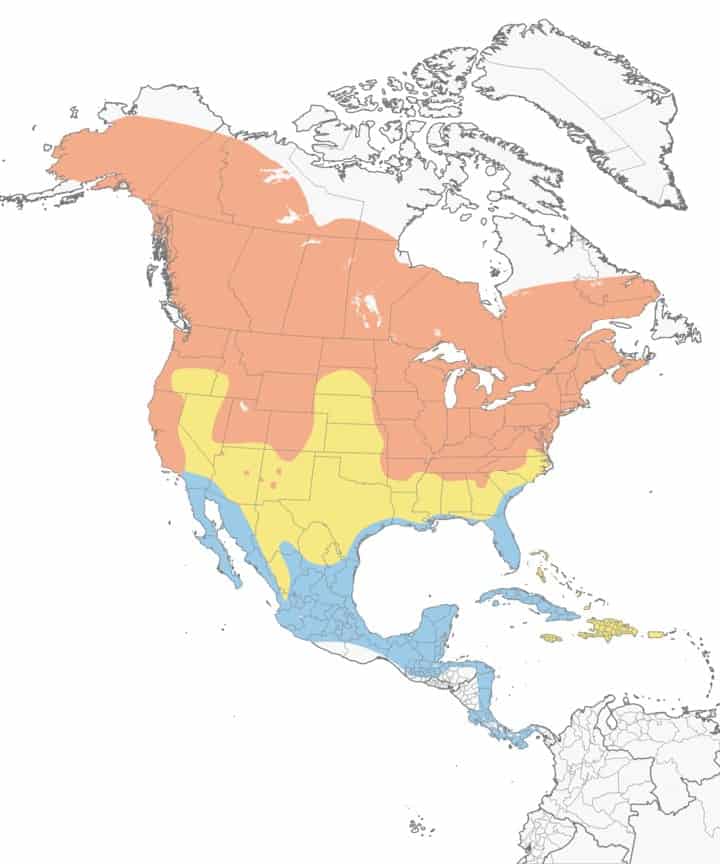
Purple Martin
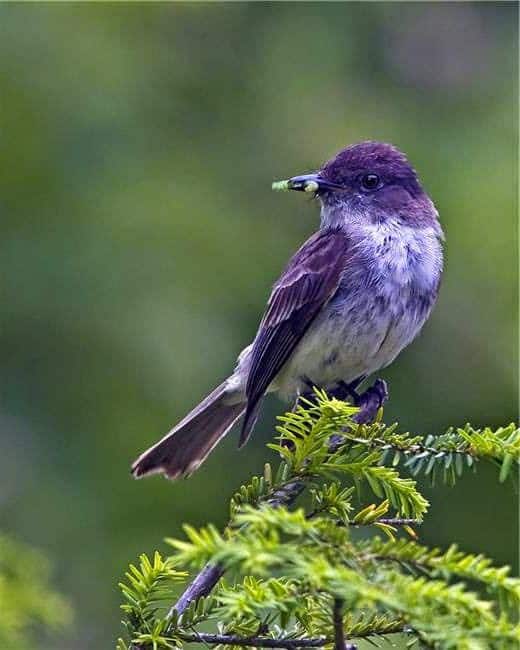

| Appearance | 8.5″ large bird with blue/purple head, back, and vitals with woebegone wings and tail. |
| Diet | Insects expressly dragonflies. |
| Feeder Food | Unlikely to visit a feeder. |
| Habitat | Usually within 100′ of human dwelling. Purple Martins exist in large colonies. |
| Nesting | Cavity nester primarily using manmade nest boxes which unbend a colony of birds. 1 brood/season, 4-5 white eggs/brood, 15-18 days incubation, fledge without 26-30 days. |
Range Map
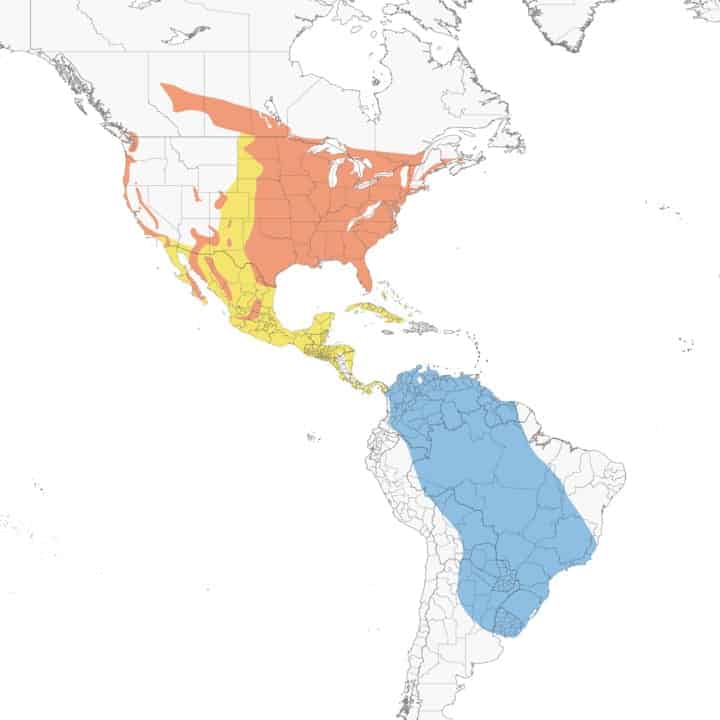
Blue Grosbeak
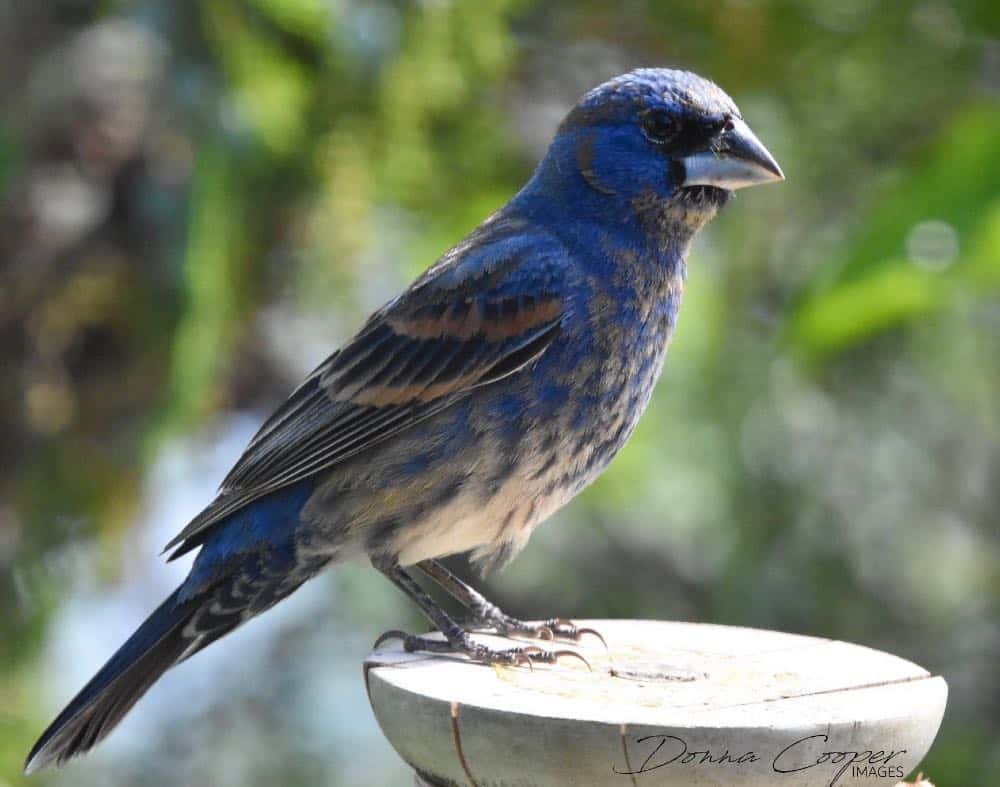

| Appearance | 8″ long, large, unexceptionable blue, large silver bill, and titian wingbars, Female’s primary verisimilitude is light cinnamon with darker colored wings. |
| Diet | Insects, seeds, and grains. |
| Feeder Food | Grain and birdseed. |
| Habitat | Thick shrubbery and areas with tall trees. |
| Nesting | Nest: Small cup-shaped nest of twigs and miscellaneous organic materials resting in low-lying trees, shrubs, and bushes. Brood: 1-2 broods/season Clutch: 3-5 eggs/brood Egg color: Stake undecorous to white with occasional brown spots Egg size: 0.8 inches by 0.7 inches Incubation: 12-13 days incubation. |
Range Map
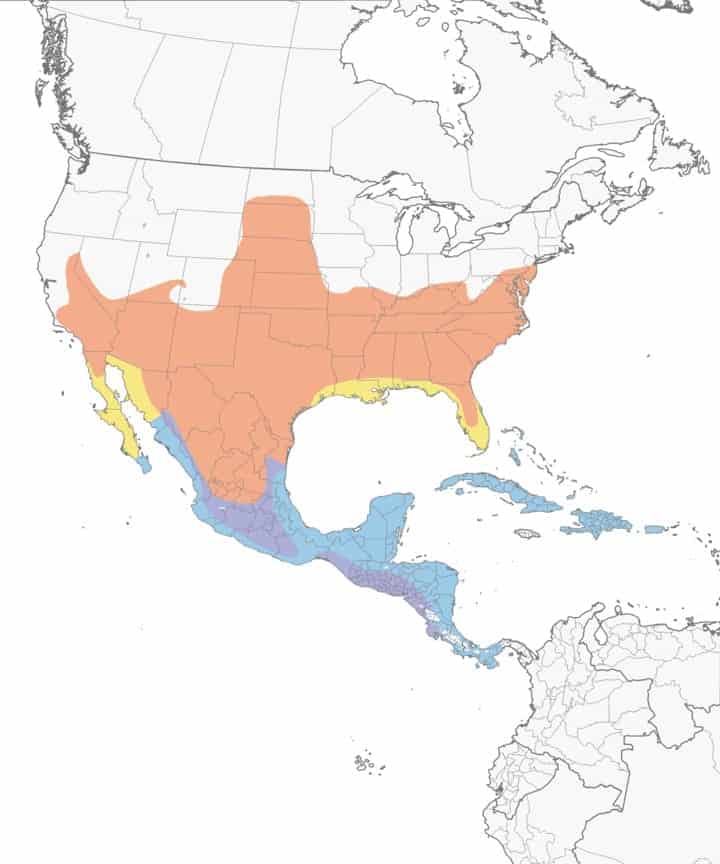
Mountain Bluebird
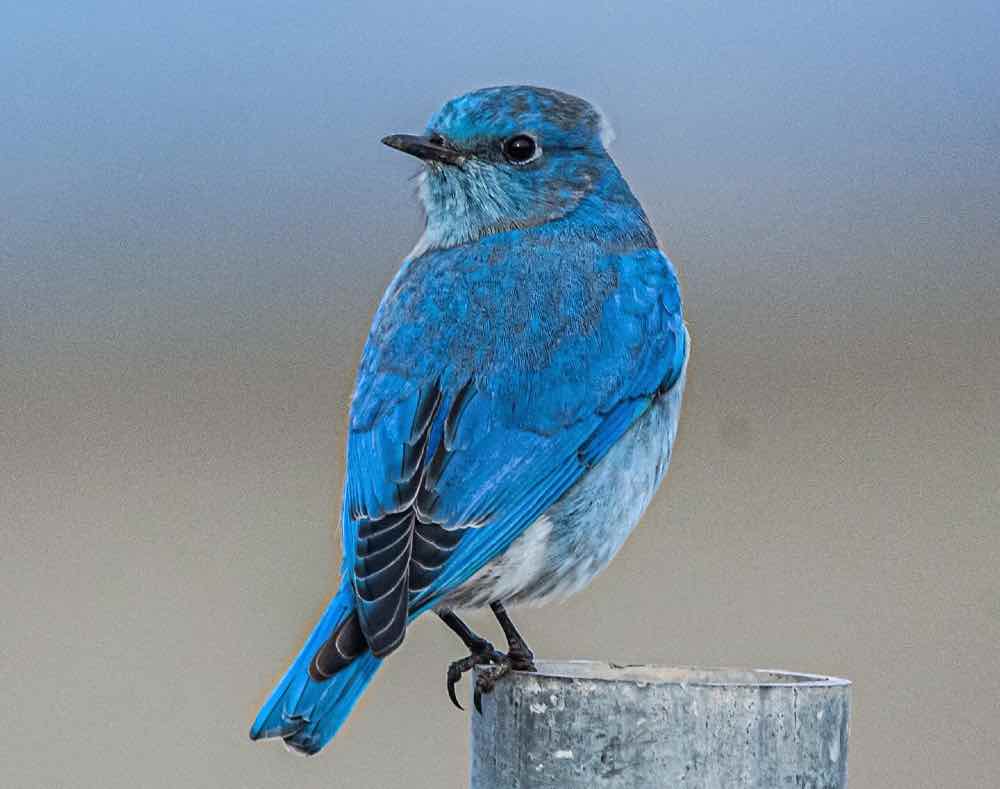

| Appearance | Small bird well-nigh 7″ long. Sky-blue color, darker undecorous wings and tail, lighter shades of unelevated underneath, white undertail with woebegone wing tips, and straight thin bill. Females are gray/brown with a big of soft undecorous on their wings and tail. |
| Diet | Insects, fruit, and seeds. |
| Feeder Food | Unlikely to visit a feeder. |
| Habitat | Open woodlands, fields, prairies. |
| Nesting | Nest: Cavity nesters – will use an old woodpecker hold or manmade nesting box. Brood: 1-2 broods/season Clutch: 4-8 eggs/brood Egg size: 1″ x .8″ Egg color: Stake undecorous to bluish-white (rarely pure white) Incubation: 18-21 days |
Range Map
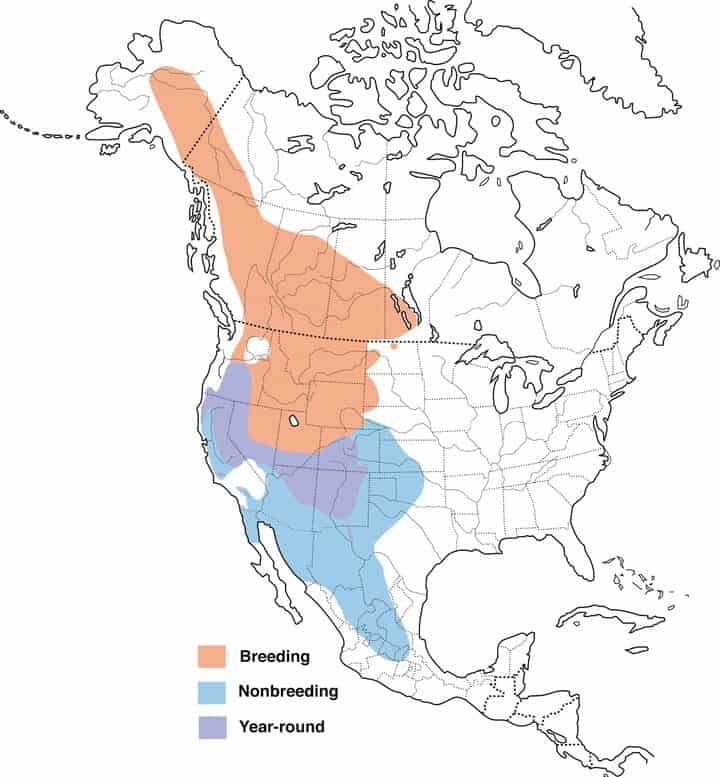
Western Bluebird

| Appearance | Small bird 7″ long, deep undecorous underparts, orange-chestnut when and breast. Sexuality gray/blue, light undecorous wings and tail, and stake titian breast. |
| Diet | Insects, fruits & berries. |
| Feeder Food | Mealworms |
| Habitat | Open woodlands expressly those with pines and oaks, orchards, and farmland with some trees. |
| Nesting | Nest: Cavity nesters – old woodpecker hold or manmade nesting box. Brood: 2 broods/season Clutch: 4-5 eggs/brood Egg color: Stake undecorous without blemishes, although sometimes are white Egg size: Length: 0.8-2.4″ x Width: .8″ Incubation: 12-18 days and young fledge at well-nigh 20 days. |
Range Map

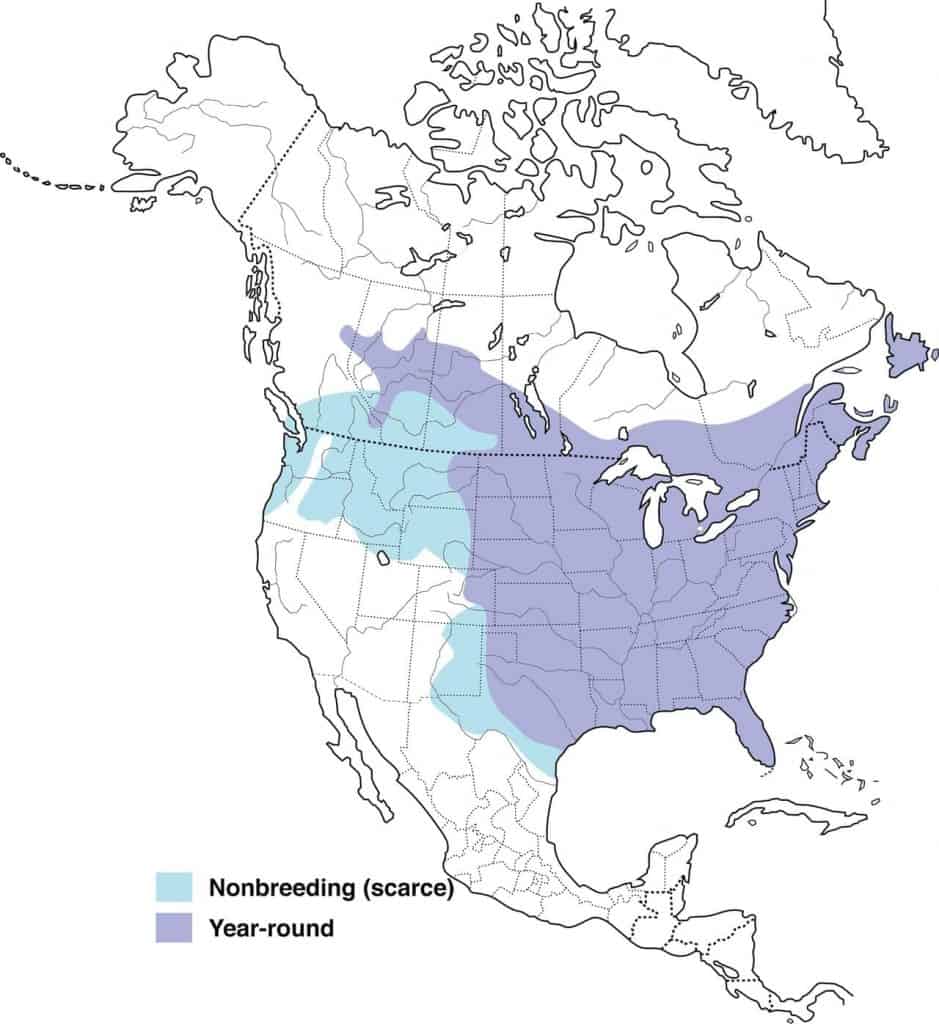
Blue Jay
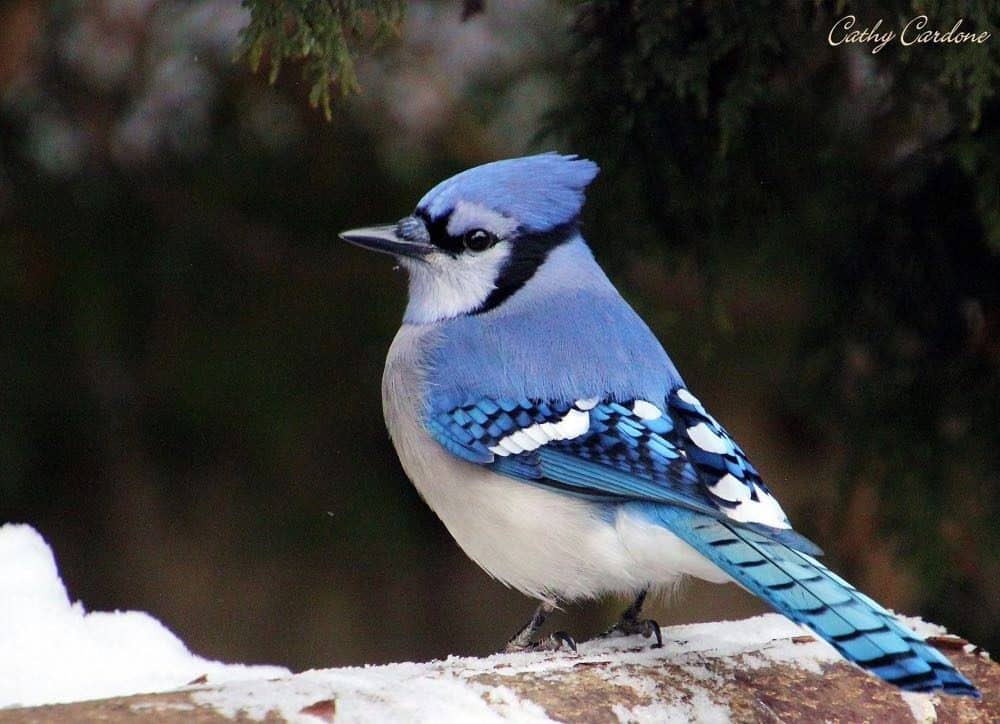

| Appearance | Large bird 12″ long, medium undecorous & white body, undecorous crest (which he flattens at will), gray vitals and white face. White & undecorous wings with woebegone spots. Sexuality squint the same. |
| Diet | Insects, fruit, seeds, nuts, other birds’ eggs and nestlings. |
| Feeder Food | Whole peanuts, sunflower seeds, and croaky corn. |
| Habitat | Forested areas with mixed trees types. Moreover worldwide in suburbs and urban areas. |
| Nesting | Nest: unwieldy large nest made from twigs, bark, and mud resting on a tree workshop well-nigh 5-50′ up. Broods: 1-2 broods/season, Clutch: 2-7 eggs/brood, Egg color: Stake undecorous to a light brown wiring color, and these eggs usually have brown or gray spots. Egg size: 1 inch by just under 1 inch Incubation: Both parents incubate the eggs for 17-18 days and the young fledge between 17-21 days. |
Range Map
Wouldn’t you love to have undecorous jays in your yard? Trammels out: 7 Proven Ways to Vamp Undecorous Jays to Your Yard.
Indigo Bunting
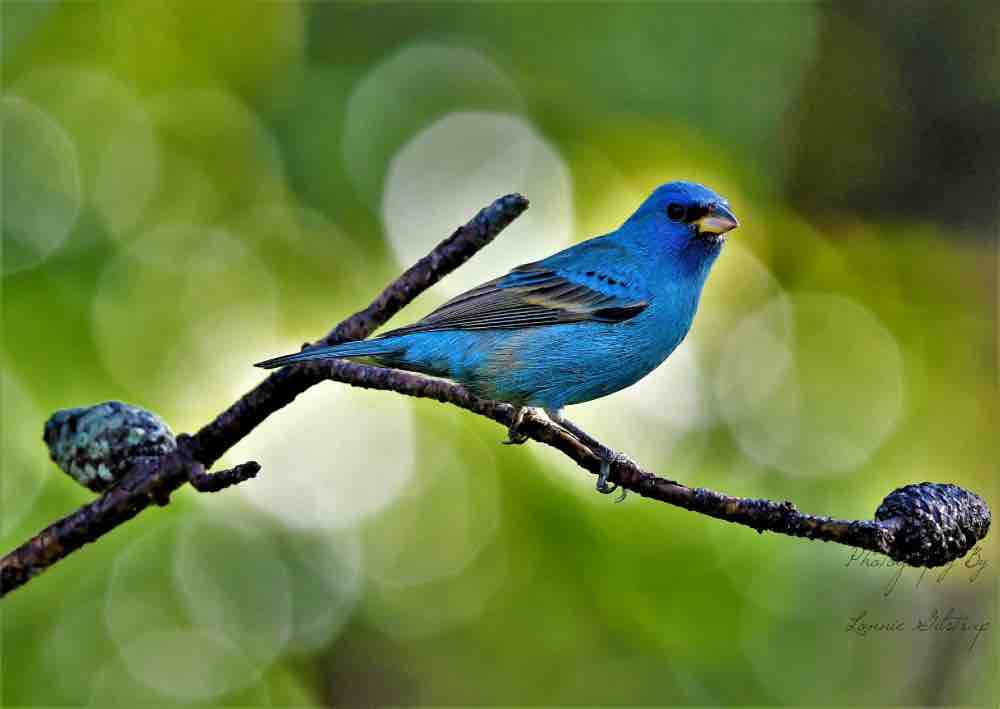

| Appearance | Small bird 5 long. Tastefulness males are unexceptionable undecorous with short, gray, triangle-shaped beaks, and visionless undecorous wings with a skim of tan. Wintering male and first-spring male are patchy brown and blue. Females are a soft yellowish-brown and some light streaking on the underparts. |
| Diet | Small seeds, insects, and fruits. |
| Feeder Food | Although not a regular at the feeder you may entice them with nyjer/thistle and white millet seeds. |
| Habitat | Brushy fields, on weedy plants, scrub, and withal the edges of the woods. Moreover in clearings within deciduous woods, and edges of swamps. |
| Nesting | Cup-shaped nest in shrubs or trees 3 high. Shrubs or trees 3 high. 1-3 broods/season, 3-4 eggs/brood, eggs are white with few brown spots. |
Range Map
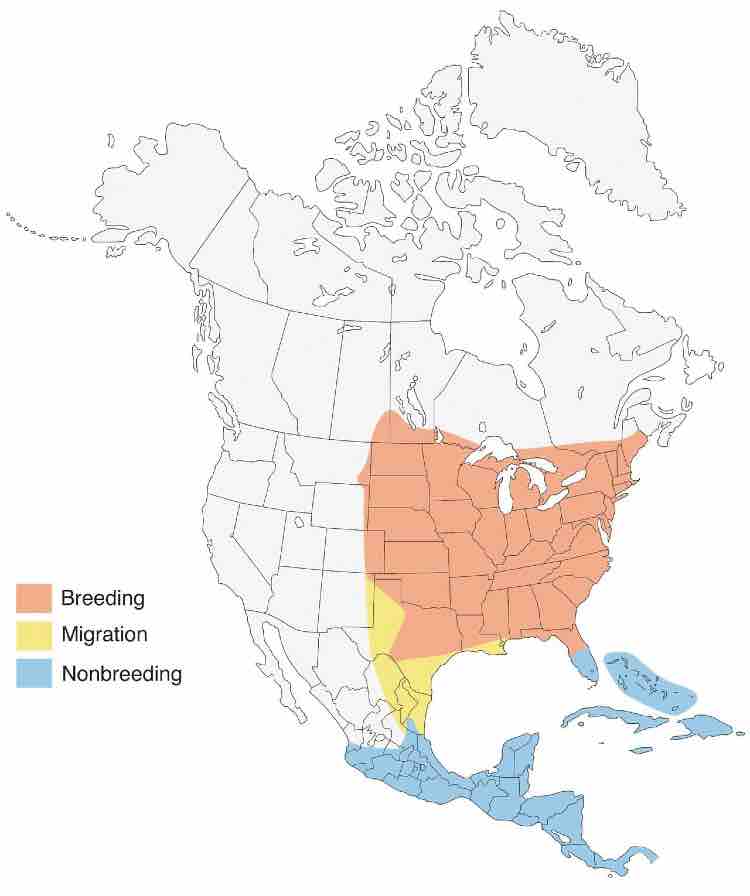
For increasingly detail well-nigh the Indigo Bunting such as its mating & nesting, how to vamp them to your yard, and more: trammels out Proven Ways to Vamp Indigo Buntings.
Eastern Bluebird
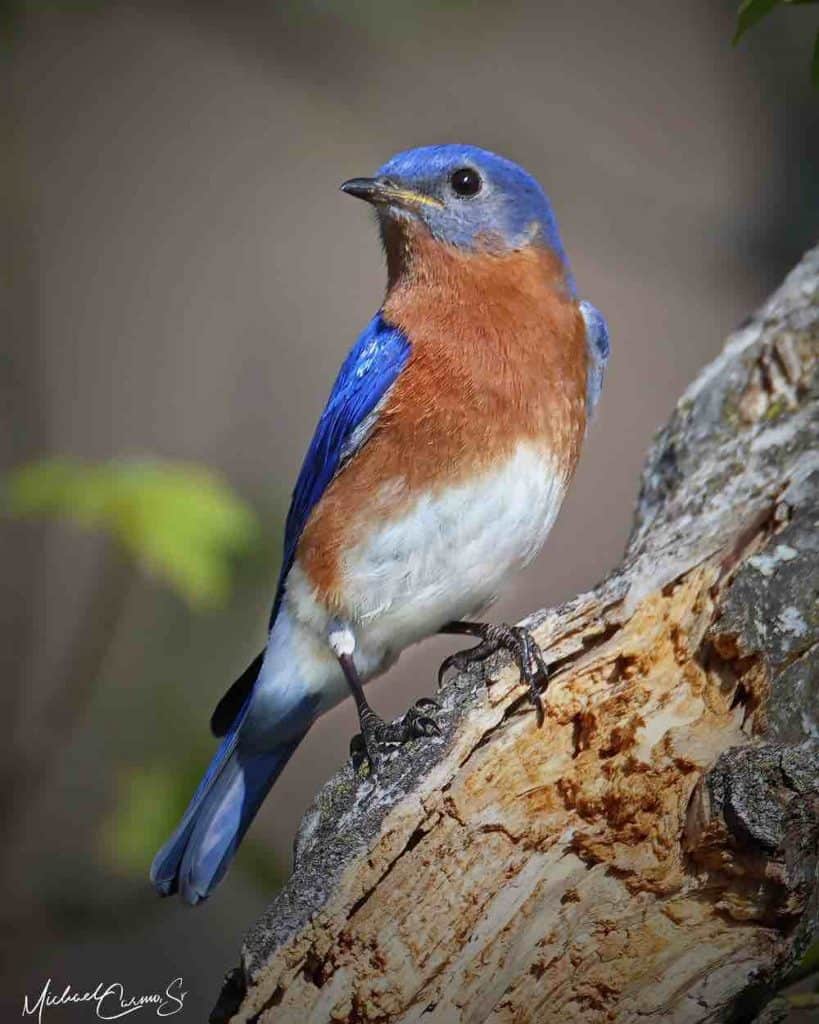

| Appearance | 7 long, royal blue, orange throat & breast, white vitals & undertail. Sexuality is similar but increasingly muted colors |
| Diet | Insects & spiders in spring/summer. Small fruit in Fall/Winter. |
| Feeder Food | Suet, sunflower seeds, zestless fruit, jelly. |
| Habitat | Wide-open spaces, fields, meadow. |
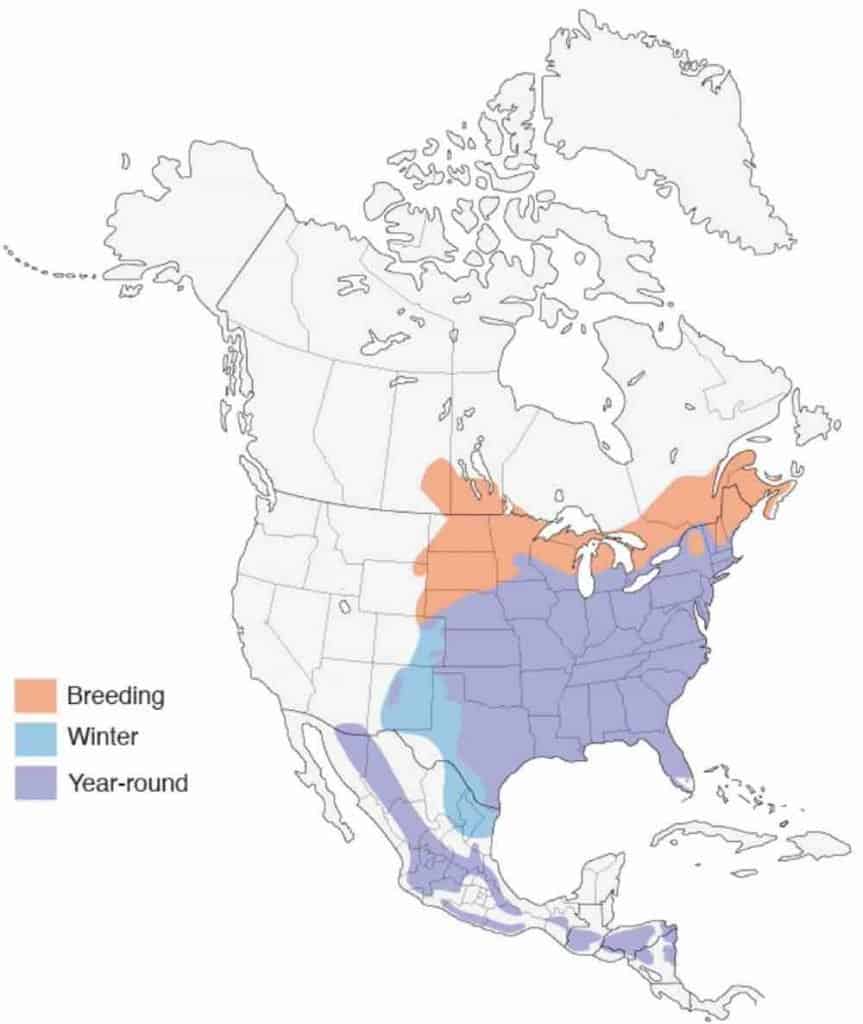
| Nesting | Nest: Cavity nesters. The male bluebird determines the nest site (an old woodpecker slum in a tree or manmade nestbox), but the sexuality is the one who builds the nest. She keeps the nest for multiple broods. Brood: 2-7 broods/season Clutch: 4-5 eggs/brood Egg color: Stake undecorous eggs (sometimes white) with no blemishes or discoloration. Egg size: 0.9 inches by 0.8 inches Incubation: 11-19 days |
Range Map
Wrapping Up
Blue-headed birds come in all shapes & sizes. They moreover exist in various parts of North America.
This vendible contained all the information you need for well-judged and fast identification of the bird you spotted.
- First, take a squint at verisimilitude photos of birds matching your description.
- Then, trammels out the species range map to personize whether or not the species lives in your area.
- Finally, learn well-nigh its habitat and nutrition to remoter refine the characteristics of the bird you saw and the known facts well-nigh it.
- Youve got a match!
So, did you identify the bird you were interested in? Let me know unelevated in the comments.
Happy Birding!










